1,1,4,4-四苯基-1,3-丁二烯

1,1,4,4-四苯基-1,3-丁二烯结构式

|
常用名 | 1,1,4,4-四苯基-1,3-丁二烯 | 英文名 | 1,1,4,4-TETRAPHENYL-1,3-BUTADIENE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 1450-63-1 | 分子量 | 358.47400 | |
| 密度 | 1.079 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 556.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C28H22 | 熔点 | 207-209 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 289ºC | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
| 中文名 | 1,1,4,4-甲苯基-1,3-丁二烯 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | 1,1,4,4-Tetraphenyl-1,3-butadiene |
| 中文别名 | 1,1',1'',1'''-(1,3-丁二烯-1,4-二基亚基)四苯 | 1,1,4,4-四苯基1,3-丁二烯 | 1,1,4,4-四苯基-1,3-丁二烯 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 密度 | 1.079 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 556.1ºC at 760 mmHg |
| 熔点 | 207-209 °C(lit.) |
| 分子式 | C28H22 |
| 分子量 | 358.47400 |
| 闪点 | 289ºC |
| 精确质量 | 358.17200 |
| LogP | 7.25020 |
| 外观性状 | 白色至黄色白色针状 |
| 蒸汽压 | 7.77E-12mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.635 |
| 储存条件 | 密封、在2 ºC -8 ºC下保存 |
| 稳定性 | 如果遵照规格使用和储存则不会分解,未有已知危险反应,避免氧化物 |
| 分子结构 | 1、 摩尔折射率:119.05 2、 摩尔体积(m3/mol):332.1 3、 等张比容(90.2K):857.8 4、 表面张力(dyne/cm): 44.4 5、 介电常数:无可用 6、 偶极距(10 -24cm 3):无可用 7、 极化率:47.19 |
| 计算化学 | 1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):8.6 2.氢键供体数量:0 3.氢键受体数量:0 4.可旋转化学键数量:5 5.互变异构体数量:无 6.拓扑分子极性表面积0 7.重原子数量:28 8.表面电荷:0 9.复杂度:412 10.同位素原子数量:0 11.确定原子立构中心数量:0 12.不确定原子立构中心数量:0 13.确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15.共价键单元数量:1 |
| 更多 | 1. 性状:带白色纤维。 2. 密度(g/mL,25/4℃): 未确定 3. 相对蒸汽密度(g/mL,空气=1):未确定 4. 熔点(ºC):207-209 5. 沸点(ºC,常压):未确定 6. 沸点(ºC,5.2kPa): 未确定 7. 折射率: 未确定 8. 闪点(ºC): 未确定 9. 比旋光度(º): 未确定 10. 自燃点或引燃温度(ºC): 未确定 11. 蒸气压(kPa,25ºC): 未确定 12. 饱和蒸气压(kPa,60ºC): 未确定 13. 燃烧热(KJ/mol):未确定 14. 临界温度(ºC): 未确定 15. 临界压力(KPa): 未确定 16. 油水(辛醇/水)分配系数的对数值: 未确定 17. 爆炸上限(%,V/V):未确定 18. 爆炸下限(%,V/V): 未确定 19. 溶解性:未确定 |
|
1,1,4,4-四苯基-1,3-丁二烯毒理学数据: 急性毒性:小鼠腹经LD50:>10gm/kg;小鼠口经LD50:>14gm/kg; 1,1,4,4-四苯基-1,3-丁二烯生态学数据: 对是水稍微有危害的不要让未稀释或大量的产品接触地下水、水道或者污水系统,若无政府许可,勿将材料排入周围环境。 |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 | Warning |
| 危害声明 | H315-H319-H335 |
| 警示性声明 | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| 个人防护装备 | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | Xi: Irritant; |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | R36/37/38 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | S26-S36 |
| 危险品运输编码 | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK德国 | 2 |
| RTECS号 | CY9040630 |
| 1,1,4,4-四苯基-1,3-丁二烯上游产品 7 | |
|---|---|
| 1,1,4,4-四苯基-1,3-丁二烯下游产品 6 | |
|
Preparation, Structural Determination, and Characterization of Electronic Properties of Bis-silylated and Bis-germylated Lu3 N@Ih -C80.
Chemistry 21 , 16411-20, (2015) Bis-silylated and bis-germylated derivatives of Lu3 N@Ih -C80 (3, 4, 5) were successfully synthesized by the photochemical addition of disiliranes 1 a, 1 b or digermirane 2, and fully characterized by... |
|
|
Replication of boid inclusion body disease-associated arenaviruses is temperature sensitive in both boid and mammalian cells.
J. Virol. 89(2) , 1119-28, (2015) Boid inclusion body disease (BIDB) is a fatal disease of boid snakes, the etiology of which has only recently been revealed following the identification of several novel arenaviruses in diseased snake... |
|
|
Ability of the Encephalitic Arbovirus Semliki Forest Virus To Cross the Blood-Brain Barrier Is Determined by the Charge of the E2 Glycoprotein.
J. Virol. 89 , 7536-49, (2015) Semliki Forest virus (SFV) provides a well-characterized model system to study the pathogenesis of virus encephalitis. Several studies have used virus derived from the molecular clone SFV4. SFV4 virus... |
| 1,4,4-triphenylbuta-1,3-dienylbenzene |
| EINECS 215-914-7 |
| MFCD00004766 |
 CAS号4541-89-3
CAS号4541-89-3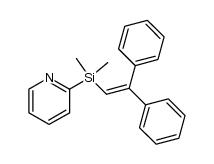 CAS号270589-02-1
CAS号270589-02-1 CAS号530-48-3
CAS号530-48-3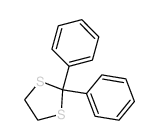 CAS号6317-10-8
CAS号6317-10-8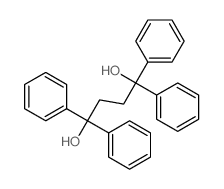 CAS号63469-15-8
CAS号63469-15-8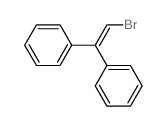 CAS号13249-58-6
CAS号13249-58-6 CAS号108-86-1
CAS号108-86-1 CAS号2491-41-0
CAS号2491-41-0 CAS号1483-64-3
CAS号1483-64-3 CAS号7476-12-2
CAS号7476-12-2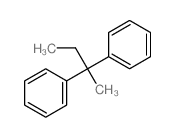 CAS号5223-61-0
CAS号5223-61-0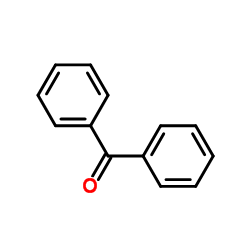 CAS号119-61-9
CAS号119-61-9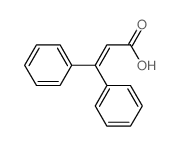 CAS号606-84-8
CAS号606-84-8
