聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺
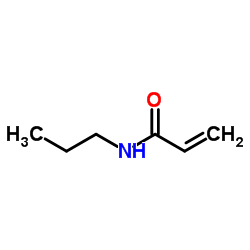
聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺结构式

|
常用名 | 聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺 | 英文名 | poly(n-isopropyl acrylamide) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 25189-55-3 | 分子量 | 113.158 | |
| 密度 | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 234.2±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C6H11NO | 熔点 | 96 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 126.0±4.8 °C |
| 中文名 | 聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺) |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) macromolecule |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 密度 | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 234.2±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 熔点 | 96 °C(lit.) |
| 分子式 | C6H11NO |
| 分子量 | 113.158 |
| 闪点 | 126.0±4.8 °C |
| 精确质量 | 113.084061 |
| PSA | 29.10000 |
| LogP | 0.38 |
| 外观性状 | 白色结晶粉末 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.1±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.430 |
| 储存条件 | 密闭于阴凉干燥环境中 |
| 稳定性 | 遵照规定使用和储存则不会分解。 |
| 分子结构 | 1、摩尔折射率:无可用 2、 摩尔体积(cm3/mol):无可用 3、 等张比容(90.2K):无可用 4、 表面张力(dyne/cm):无可用 5、 极化率:无可用 |
| 计算化学 | 1、 疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):1 2、 氢键供体数量:1 3、 氢键受体数量:1 4、 可旋转化学键数量:3 5、 拓扑分子极性表面积(TPSA):29.1 6、 重原子数量:8 7、 表面电荷:0 8、 复杂度:88.5 9、 同位素原子数量:0 10、 确定原子立构中心数量:0 11、 不确定原子立构中心数量:0 12、 确定化学键立构中心数量:0 13、 不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14、 共价键单元数量:1 |
| 更多 | 1. 性状:无可用 2. 密度(g/mL,25/4℃):无可用 3. 相对蒸汽密度(g/mL,空气=1):无可用 4. 溶解性:无可用 5. 沸点(ºC,常压):无可用 6. 沸点(ºC,5.2kPa):无可用 7. 折射率:无可用 8. 闪点(ºC):无可用 9. 比旋光度(º):无可用 10. 自燃点或引燃温度(ºC):无可用 11. 蒸气压(kPa,25ºC):无可用 12. 饱和蒸气压(kPa,60ºC):无可用 13. 燃烧热(KJ/mol):无可用 14. 临界温度(ºC):无可用 15. 临界压力(KPa):无可用 16. 油水(辛醇/水)分配系数的对数值:无可用 17. 爆炸上限(%,V/V):无可用 18. 爆炸下限(%,V/V):无可用 |
| 个人防护装备 | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| 危险品运输编码 | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK德国 | 1 |
|
Label-free detection of low protein concentration in solution using a novel colorimetric assay.
Biosens. Bioelectron. 49 , 133-8, (2013) Dual pH and temperature sensitive microgel-based etalons were fabricated by sandwiching a "monolithic" microgel layer between two semitransparent, Au layers. The devices exhibit visual color and multi... |
|
|
Mechanistic insights into amplification of specific ion effect in water-nonaqueous solvent mixtures.
J. Phys. Chem. B 117(8) , 2535-44, (2013) Ethylene glycol (EG) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) can act as both hydrogen-bond donors and acceptors in the formation of solvent complexes with water molecules. In the present work, we have systematic... |
|
|
Tailoring enzyme activity and stability using polymer-based protein engineering.
Biomaterials 34(30) , 7437-43, (2013) Polymer-based protein engineering (PBPE) offers an attractive method to predictably modify and enhance enzyme structure and function. Using polymers that respond to stimuli such as temperature and pH,... |
| MFCD00284282 |

