二丙二醇甲醚
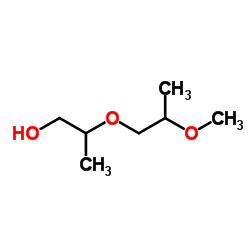
二丙二醇甲醚结构式

|
常用名 | 二丙二醇甲醚 | 英文名 | Dipropylene glycol monomethyl ether |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 34590-94-8 | 分子量 | 148.200 | |
| 密度 | 0.951 | 沸点 | 190 ºC | |
| 分子式 | C7H16O3 | 熔点 | -80°C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 166 ºF |
二丙二醇甲醚用途【用途一】 用作硝化纤维素、乙基纤维素、聚醋酸乙烯酯等的溶剂 【用途二】
涂料、染料的溶剂,也是刹车油组分。 更多
|
| 中文名 | 二丙二醇甲醚 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | Dipropylene glycol monomethyl ether |
| 中文别名 | 一缩二丙二醇单甲醚 | 二丙二醇单甲醚 | 一缩二丙二醇一甲醚 | 甲氧基二丙二醇 | 缩水二丙二醇一甲醚 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 密度 | 0.951 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 190 ºC |
| 熔点 | -80°C |
| 分子式 | C7H16O3 |
| 分子量 | 148.200 |
| 闪点 | 166 ºF |
| 精确质量 | 148.109940 |
| PSA | 38.69000 |
| LogP | -0.46 |
| 外观性状 | 无色液体带有温和令人愉快的气味 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.1±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.422 |
| 储存条件 | 包装完整、轻装轻卸,库房通风、远离明火、高温、与氧化剂分开存放 |
| 稳定性 | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| 分子结构 | 1、 摩尔折射率:39.50 2、 摩尔体积(cm3/mol):154.3 3、 等张比容(90.2K):366.7 4、 表面张力(dyne/cm):31.8 5、 介电常数: 6、 偶极距(10-24cm3): 7、 极化率:15.66 |
| 计算化学 | 1、 疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):0.7 2、 氢键供体数量:1 3、 氢键受体数量:3 4、 可旋转化学键数量:6 5、 互变异构体数量: 6、 拓扑分子极性表面积(TPSA):38.7 7、 重原子数量:10 8、 表面电荷:0 9、 复杂度:65.9 10、同位素原子数量:0 11、确定原子立构中心数量:0 12、不确定原子立构中心数量:1 13、确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14、不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15、共价键单元数量:1 |
| 更多 | 1. 性状:无色透明粘稠液体 2. 密度(g/mL,25/25℃):0.954 3. 相对蒸汽密度(g/mL,空气=1):5.11 4. 熔点(ºC):-80 5. 沸点(ºC,常压):190 6. 沸点(ºC,1.6KPa):90-91 7. 折射率(25ºC):1.419 8. 闪点(ºC,开口):85 9. 黏度(mPa·s,25ºC):3.33 10. 蒸气压(KPa,25ºC):0.05 11. 溶解性:与水混溶。能溶解油脂、橡胶、天然树脂乙基纤维素、硝酸纤维素、聚乙酸乙烯酯、聚乙烯醇缩丁醛、醇酸树脂、酚醛树脂、尿素树脂等。 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
二丙二醇甲醚毒理学数据: 1、 皮肤、眼睛刺激毒性:人经眼Draize标准实验:8mg 兔子皮肤开放式刺激实验:500mg 兔子经眼Draize标准实验:500mg/24H 2、 急性毒性:大鼠经口LD50:5400mL/kg;狗经口LD50:7500mg/kg 兔子皮肤LD50:10mL/kg 3、 其他多剂量毒性:兔子皮肤TDLo:650mg/kg/13W-I 4、属低毒类,雄大鼠经口LD50为5.50mL/kg,雌大鼠经口LD50为5.45mL/kg。动物中毒表现以中枢神经抑制为主,死于呼吸衰竭。 |
| 个人防护装备 | Eyeshields;Gloves;half-mask respirator (US);multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US) |
|---|---|
| 危害码 (欧洲) | Xi |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | S23-S24/25 |
| 危险品运输编码 | NA 1993 / PGIII |
| WGK德国 | 1 |
| RTECS号 | JM1575000 |
| 海关编码 | 29094919 |
1、 由1,2-环氧丙烷水合生成一缩二丙二醇,再与甲醇反应而得。另一种方法是将1,2-环氧丙烷在BF3催化下与甲醇反应,调整甲醇配比,先水解成一缩二丙二醇,再进一步反应生成本品。
精制方法:分馏精制。
| 海关编码 | 29094919 |
|---|
|
Modeling aggregate exposures to glycol ethers from use of commercial floor products.
Int. J. Toxicol. 25(2) , 95-107, (2006) Computer modeling of aggregate exposure provides the capability to estimate the range of doses that can occur from product use and to understand the relative importance of different routes of exposure... |
|
|
Final report on the safety assessment of PPG-2 methyl ether, PPG-3 methyl ether, and PPG-2 methyl ether acetate.
Int. J. Toxicol. 28(6 Suppl) , 162S-74S, (2009) PPG-2 methyl ether, PPG-3 methyl ether, and PPG-2 methyl ether acetate are used in cosmetics as fragrance ingredients and/or solvents at concentrations of 0.4% to 2%. Propylene glycol ethers are rapid... |
|
|
Critical effects and exposure limits.
Risk Anal. 17(2) , 227-36, (1997) The use of critical effects in the determination of occupational exposure limits (OELs) in Sweden is subjected to a statistical study. Many of the present OELs are high in relation to known no-effect ... |
| 2-(2-Methoxypropoxy)propan-1-ol |
| DPM |
| 2-(2-Methoxypropoxy)-1-propanol |
| Methoxypropoxypropanol |
| dowanoldpm |
| dpgme |
| 1-Propanol, 2-(2-methoxypropoxy)- |
| CHEM-CLEAR |
| MFCD00059604 |
| Q1Y1&O1Y1&O1 |
| kino-red |
| Dipropylene glycol monomethyl ethe |
| Dipropylene glycol monomethyl ether |
| dowanol50b |
| CHEM-CLEAR(R) |
| Di(propylene glycol) methyl ether |
| EINECS 252-104-2 |
| arcosolv |
| Arcosolv DPM |


