特屈儿
一般危化品
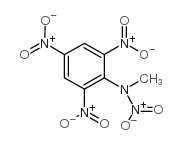
特屈儿结构式
|
常用名 | 特屈儿 | 英文名 | tetryl |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 479-45-8 | 分子量 | 287.14300 | |
| 密度 | 1.803g/cm3 | 沸点 | 503.7ºC at 760mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C7H5N5O8 | 熔点 | 130ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | 闪点 | 258.4ºC | |
| 符号 |


GHS02, GHS07 |
信号词 | Danger |
特屈儿用途1.有良好引爆能力,用于引爆药及猛烈炸药。由于毒性较大,已逐渐被太安、黑索今等炸药取代,但仍作为传爆药柱的装药。 2.用作引爆药、导爆索及雷管的副装药、指示剂。 |
| 中文名 | 特屈儿 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | N-methyl-N-picrylnitramine |
| 中文别名 | 硝基胺 | 2,4,6-三硝基苯甲硝 | N-甲-N,2,4,6-四硝苯胺 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 密度 | 1.803g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 503.7ºC at 760mmHg |
| 熔点 | 130ºC |
| 分子式 | C7H5N5O8 |
| 分子量 | 287.14300 |
| 闪点 | 258.4ºC |
| 精确质量 | 287.01400 |
| PSA | 186.52000 |
| LogP | 3.13190 |
| 折射率 | 1.686 |
| 储存条件 | 储存注意事项 为安全起见,储存时可加不少于15%的水作稳定剂。储存于阴凉、干燥、通风的爆炸品专用库房。远离火种、热源。若含有水作稳定剂,库温不低于1℃,相对湿度小于80%。应与还原剂、碱类等分开存放,切忌混储。采用防爆型照明、通风设施。禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储区应备有合适的材料收容泄漏物。禁止震动、撞击和摩擦。 |
| 稳定性 | 1.稳定性 稳定 2.禁配物 强还原剂、强碱、肼 3.避免接触的条件 热、摩擦、震动和撞击 4.聚合危害 不聚合 5.分解产物 氮氧化物、氨 |
| 分子结构 | 1、摩尔折射率:61.59 2、摩尔体积(cm3/mol):159.2 3、等张比容(90.2K):494.5 4、表面张力(dyne/cm):93.0 5、介电常数:无可用的 6、极化率(10-24cm3):24.41 7、单一同位素质量:287.013812 Da 8、标称质量:287 Da 9、平均质量:287.1433 Da |
| 计算化学 | 1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):1.7 2.氢键供体数量:0 3.氢键受体数量:9 4.可旋转化学键数量:1 5.互变异构体数量:无 6.拓扑分子极性表面积187 7.重原子数量:20 8.表面电荷:0 9.复杂度:409 10.同位素原子数量:0 11.确定原子立构中心数量:0 12.不确定原子立构中心数量:0 13.确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15.共价键单元数量:1 |
| 更多 | 1.性状:白色或黄色晶状粉末 2.熔点(℃):130~132 3.沸点(℃):187(爆炸) 4.相对密度(水=1):1.57(19℃)[4] 5.相对蒸气密度(空气=1):9.92 6.饱和蒸气压(kPa):<0.135(20℃) 7.燃烧热(kJ/mol):-3520.8 8.临界压力(MPa):2.61 9.辛醇/水分配系数:1.64 10.闪点(℃):135 11.引燃温度(℃):257 12.溶解性:不溶于水,溶于乙醇、乙醚、苯、冰醋酸。 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
特屈儿毒理学数据: 1.急性毒性 暂无资料 2.刺激性 暂无资料 3.其他 LDLo:5000mg/kg(大鼠经口) 特屈儿生态学数据: 1.生态毒性 暂无资料 2.生物降解性 暂无资料 3.非生物降解性 暂无资料 |
| 符号 |


GHS02, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 | Danger |
| 危害声明 | H225-H302 + H312 + H332-H319 |
| 警示性声明 | P210-P261-P302 + P352 + P312-P304 + P340 + P312-P337 + P313-P403 + P235 |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | E,T,F |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | 2-23/24/25-33-36/37/38-11 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | 35-45-27-16 |
| 危险品运输编码 | 0208 |
| WGK德国 | 3 |
| 危险类别 | 1.1 |
| 特屈儿上游产品 10 | |
|---|---|
| 特屈儿下游产品 10 | |
由二甲基苯胺经中和、硝化、稀释、精制制得,也可由二硝基氯苯与甲胺在苯中缩合,然后再进行硝化制得。
|
Measurement of nitrosamine and nitramine formation from NOx reactions with amines during amine-based carbon dioxide capture for postcombustion carbon sequestration.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 46(17) , 9793-801, (2012) With years of full-scale experience for precombustion CO(2) capture, amine-based technologies are emerging as the prime contender for postcombustion CO(2) capture. However, concerns for postcombustion... |
|
|
Evaluation of a TiO2 photocatalysis treatment on nitrophenols and nitramines contaminated plant wastewaters by solid-phase extraction coupled with ESI HPLC-MS.
J. Hazard. Mater. 166(1) , 284-90, (2009) Nitration reactions of aromatic compounds are commonly involved in different industrial processes for pharmaceutical, pesticide or military uses. For many years, most of the manufacturing sites used l... |
|
|
A reliable simple method to estimate density of nitroaliphatics, nitrate esters and nitramines.
J. Hazard. Mater. 169(1-3) , 158-69, (2009) In this work, a new simple method is presented to estimate crystal density of three important classes of explosives including nitroalphatics, nitrate esters and nitramines. This method allows reliable... |
| N-METHYL-N,2,4,6-TETRANITROANILINE |
| Nitramine |
| 2,4,6-trinitrophenylmethylnitramine |
| EINECS 207-531-9 |
| 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl-N-methylnitramine |
| N-methyl-N-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)nitramide |
| 2,4,6-Tetryl |
| N-Methyl-N-picrylnitramine |
| Picrylmethylnitramine |
| Tetril |
| Tetralite |
| N-Picryl-N-methylnitramine |
| Picrylnitromethylamine |
| Tetryl |
| N-2,4,6-tetranitro-N-methylaniline |

 CAS号19406-51-0
CAS号19406-51-0 CAS号7664-93-9
CAS号7664-93-9 CAS号2044-88-4
CAS号2044-88-4 CAS号121-69-7
CAS号121-69-7 CAS号612-28-2
CAS号612-28-2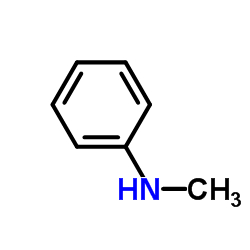 CAS号100-61-8
CAS号100-61-8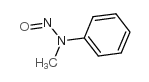 CAS号614-00-6
CAS号614-00-6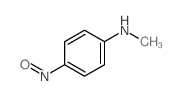 CAS号10595-51-4
CAS号10595-51-4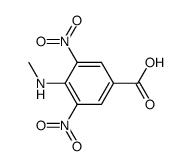 CAS号64732-83-8
CAS号64732-83-8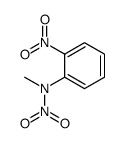 CAS号102877-65-6
CAS号102877-65-6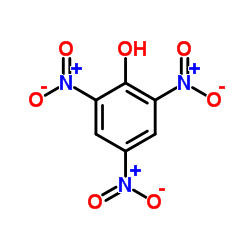 CAS号88-89-1
CAS号88-89-1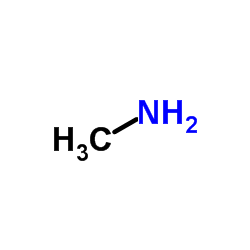 CAS号74-89-5
CAS号74-89-5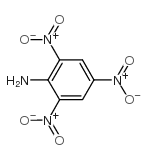 CAS号489-98-5
CAS号489-98-5 CAS号7697-37-2
CAS号7697-37-2 CAS号7782-77-6
CAS号7782-77-6 CAS号1022-07-7
CAS号1022-07-7 CAS号857592-15-5
CAS号857592-15-5 CAS号16552-38-8
CAS号16552-38-8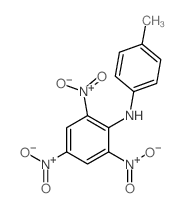 CAS号16552-37-7
CAS号16552-37-7 CAS号57205-99-9
CAS号57205-99-9