Pyridaben-d13
Modify Date: 2024-01-05 17:52:26
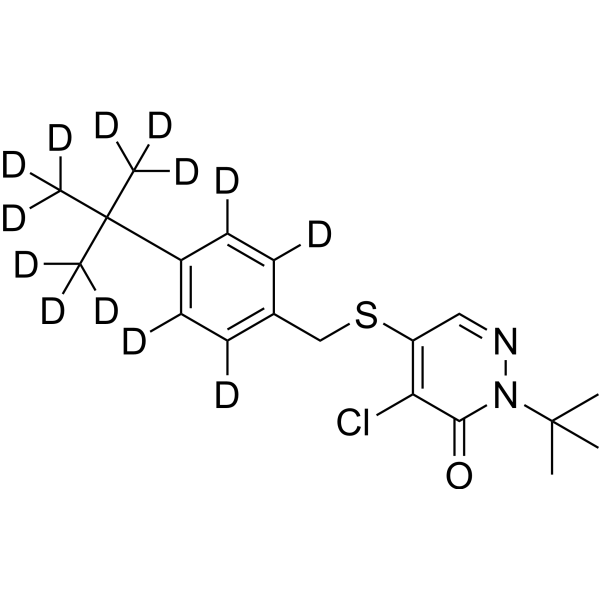
Pyridaben-d13 structure
|
Common Name | Pyridaben-d13 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2468638-05-1 | Molecular Weight | 378.01 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H12D13ClN2OS | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Pyridaben-d13Pyridaben-d13 is the deuterium labeled Pyridaben[1]. Pyridaben is a mitochondrial electron transport inhibitor (METI) acaricide that promotes the formation of damaging oxygen and nitrogen radicals. Pyridaben selectively inhibits complex I (NADH dehydrogenase) with an IC50 value of 2.4 nM (assay sites: rat liver and bovine heart mitochondria). Pyridaben also significantly inhibits rat mitochondrial mtNOS function[2][3]. |
| Name | Pyridaben-d13 |
|---|
| Description | Pyridaben-d13 is the deuterium labeled Pyridaben[1]. Pyridaben is a mitochondrial electron transport inhibitor (METI) acaricide that promotes the formation of damaging oxygen and nitrogen radicals. Pyridaben selectively inhibits complex I (NADH dehydrogenase) with an IC50 value of 2.4 nM (assay sites: rat liver and bovine heart mitochondria). Pyridaben also significantly inhibits rat mitochondrial mtNOS function[2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C19H12D13ClN2OS |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 378.01 |