197794-83-5
| Name | tfllr-nh2 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
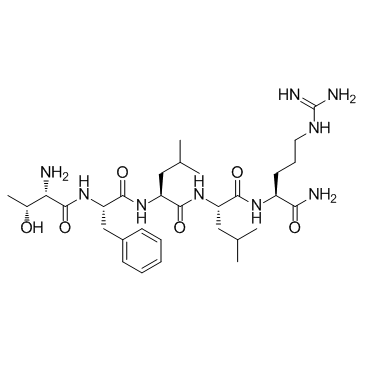
H-THR-PHE-LEU-LEU-ARG-NH2
TFLLR-AMIDE THR-PHE-LEU-LEU-ARG-NH2 REF DUPL: H-Thr-Phe-Leu-Leu-Arg-NH2 |
| Description | TFLLR-NH2 is a selective PAR1 agonist with an EC50 of 1.9 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
EC50: 1.9 μM (PAR1)[1] |
| In Vitro | PAR1 agonists stimulate concentration-dependent increases in [Ca2+]i and in the proportions of neurones. The maximal increase in [Ca2+]i above basal is detected in response to 10 μm TF-NH2(peak 196.5±20.4 nM, n=25) when 50–80% of identified neurones responded[1]. SW620 cells cultured in the supernatant of TFLLR-NH2-activated platelets upregulate E-cadherin expression and downregulate the vimentin expression. In the in vitro platelet culture system, a TFLLR-NH2 dose-dependent increase of secreted TGF-β1 is detected in the supernatant[2]. |
| In Vivo | Injection of TF-NH2 into the rat paw stimulates a marked and sustained oedema. An NK1R antagonist and ablation of sensory nerves with capsaicin inhibit oedema by 44% at 1 h and completely by 5 h. In wild-type but not PAR1−/− mice, TF-NH2 stimulates Evans blue extravasation in the bladder, oesophagus, stomach, intestine and pancreas by 2–8 fold. Extravasation in the bladder, oesophagus and stomach is abolished by an NK1R antagonist[1]. TFp-NH2 produces notable contraction at 3-50 μM and relaxation at 0.3-50 μM, in the absence of apamin. The concentration-response curve for TFp-NH2-induced contraction is remarkably shifted left, when the TFp-NH2-induced relaxation is blocked by apamin at 0.1 μM[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: Mice are anaesthetized with isofluorane, and saline or TF-NH2 (3 μmol/kg in 25 μL physiological saline) is injected into the lateral tail vein. Evans blue (33.3 mg/kg in 50 μL saline) is co-injected with the peptide. Mice are perfused transcardially at 10 min after administration of TF-NH2 with physiological saline containing 20 u/mL heparin at a pressure of 80-100 mmHg for 2-3 min. Excised tissues are incubated in 1 mL of formamide for 48 h, and Evans blue content is measured spectrophotometrically at 650 nm[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C31H53N9O6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 647.80900 |
| Exact Mass | 647.41200 |
| PSA | 267.64000 |
| LogP | 2.87230 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |