908305-13-5
| Name | Epertinib |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
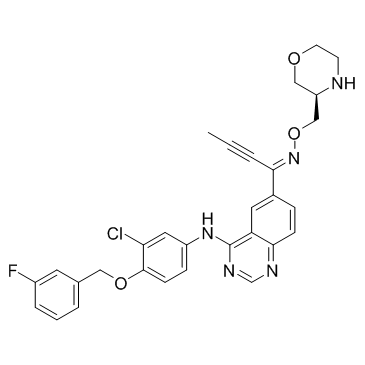
N-{3-Chloro-4-[(3-fluorobenzyl)oxy]phenyl}-6-{(1Z)-N-[(3R)-3-morpholinylmethoxy]-2-butynimidoyl}-4-quinazolinamine
2-Butyn-1-one, 1-[4-[[3-chloro-4-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]phenyl]amino]-6-quinazolinyl]-, O-[(3R)-3-morpholinylmethyl]oxime, (1Z)- Epertinib |
| Description | Epertinib is a potent, oral, reversible, and selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor of EGFR, HER2 and HER4, with IC50s of 1.48 nM, 7.15 nM and 2.49 nM, respectively; Epertinib shows potent antitumor activity. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
EGFR:1.48 nM (IC50) HER2:2.49 nM (IC50) HER4:7.15 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Epertinib (S-222611) is a potent, oral, reversible, and selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor of EGFR, HER2 and HER4, with IC50s of 1.48 nM, 7.15 nM and 2.49 nM, respectively, and shows no effect on KDR, IGF1R, SRC, KIT, and PDGFRβ (IC50, >10000 nM). Epertinib inhibits relative phosphorylation of EGFR and HER2 in NCI-N87 cells, with IC50s of 4.5 and 1.6 nM, respectively. Furthermore, Epertinib exhibits inhibitory activity against the growth of cancer cell lines expressing EGFR and/or HER2, with IC50s of 8.3 nM (NCI-N87 (stomach)), 9.9 nM (BT-474 (breast)), and 14 nM (SK-BR-3 (breast))[1]. Epertinib also inhibits MDA-MB-361 cell growth, with an IC50 of 26.5 nM[2]. |
| In Vivo | Epertinib shows antitumor activity in nude mice bearing NCI-N87 xenograft via oral administration for 21 days, with an ED50 of 10.2 mg/kg. Epertinib (50 mg/kg, p.o.) is four times more potent activity than lapatinib and completely inhibits the growth of cancer cells in mice[1]. Epertinib (50 mg/kg, p.o.) markedly reduces the brain tumor volume in the breast cancer intraventricular injection mouse brain metastasis model (IVM)[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 701.5±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C30H27ClFN5O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 560.018 |
| Flash Point | 378.0±35.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 559.178650 |
| LogP | 6.09 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.630 |