425642-32-6
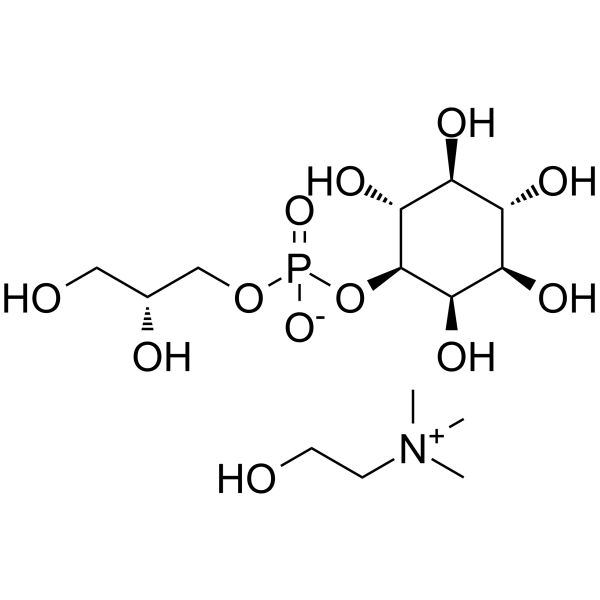
| Name | GLYCEROPHOSPHOINOSITOL CHOLINE |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
GLYCEROPHOSPHOINOSITOL CHOLINE
2-Hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium (2R)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl (1S,2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxycyclohexyl phosphate |
| Description | Glycerophosphoinositol choline is an essential nutrient that activates alpha7 nicotinic receptors and has analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity. Glycerophosphoinositol choline can affect diseases such as liver disease, atherosclerosis and neurological disorders[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Glycerophosphoinositol choline (0 or 70 μM, 4 days) can effectively mitigate apoptosis and maintain cell viability[1]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: Rat pheochromocytoma cells PC12 Concentration: 0 or 70 μM Incubation Time: 4 days Result: Showed the cell viability of 94% at 70 μM while cell viability of 83% at 0 μM. Reduced the number of cells with DNA breaks (characteristic of apoptosis) by 8.5% at 70 μM compared to the no treatment group. |
| In Vivo | Glycerophosphoinositol choline (s.c., 0.2 and 100 mg/kg/h, 24 or 48 hours) can reduce postoperative injurious reflexes and effectively decreases tumor necrosis factor (TNF) release from macrophages in female C57/Bl6 mice[2]. Animal Model: Postoperative pain model of female C57/Bl6 mice[2] Dosage: 0.2 and 100 mg/kg/h Administration: Subcutaneous injection, 24 or 48 hours Result: Reduced heat hypersensitivity after surgery with maximal efficacy after 48 h treatment and the ED50 value of choline dose was 1.7 mg/kg/h. Reduced hypersensitivity to punctate mechanical stimuli 48 hours after infusion in a dose-dependent manner and with the ED50 value of 4.7 mg/kg/h but not 24 hours. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C14H32NO12P |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 437.377 |
| Exact Mass | 437.166199 |