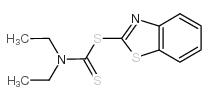
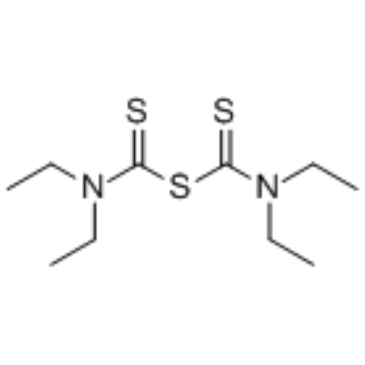
97-77-8
| Name | disulfiram |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
1,1',1'',1'''-[Disulfanediylbis(carbonothioylnitrilo)]tetraethan
Etabus Ethane, 1,1',1'',1'''-[dithiobis(carbonothioylnitrilo)]tetrakis- TTD Teturamin 1,1',1'',1'''-[Disulfanediylbis(carbonothioylnitrilo)]tetraethane Antabuse tetraethylthioperoxydicarbonic diamide ([[(C2H5)2N]C(S)]2S2) N1,N1,N3,N3-tetraethyl-2-dithioperoxy-1,3-dithiodicarbonic diamide 1,1',1'',1'''-[disulfanediylbis(carbonothioylnitrilo)]tétraéthane Tetraethylthiuran disulfide Disulfiram Tetraethylthiuram disulfide EINECS 202-607-8 MFCD00009048 tetraethylthiuram disulphide Esperal |
| Description | Disulfiram is a specific inhibitor of?aldehyde-dehydrogenase (ALDH1), used for the treatment of chronic alcoholism by producing an acute sensitivity to alcohol. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Disulfiram-copper complex potently inhibits the proteasomal activity in cultured breast cancer MDA-MB-231 and MCF10DCIS.com cells, but not normal, immortalized MCF-10A cells, before induction of apoptotic cancer cell death[1]. Disulfiram (DS), a clinically used anti-alcoholism drug, strongly inhibits constitutive and 5-FU-induced NF-kappaB activity in a dose-dependent manner. Disulfiram inhibits both NF-kappaB nuclear translocation and DNA binding activity but has no effect on 5-FU-induced IkappaBalpha degradation. Disulfiram significantly enhances the apoptotic effect of 5-FU on DLD-1 and RKO(WT) cell lines and synergistically potentiated the cytotoxicity of 5-FU to both cell lines. Disulfiram also effectively abolishes 5-FU chemoresistance in a 5-FU resistant cell line H630(5-FU) in vitro[2]. Oseltamivir decreases the number of viable cells, and the addition of CuCl2 significantly enhances the DSF-induced cell death to less than 10% of control[3]. Disulfiram given to melanoma cells in combination with Cu2+ or Zn2+ decreases expression of cyclin A and reduces proliferation in vitro at lower concentrations than disulfiram alone[4]. |
| In Vivo | Disulfiram significantly inhibits the tumor growth (by 74%), associated with in vivo proteasome inhibition (as measured by decreased levels of tumor tissue proteasome activity and accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins and natural proteasome substrates p27 and Bax) and apoptosis induction (as shown by caspase activation and apoptotic nuclei formation) in mice bearing MDA-MB-231 tumor xenografts[1]. Disulfiram blocks the P-glycoprotein extrusion pump, inhibits the transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB, sensitizes tumors to chemotherapy, reduces angiogenesis, and inhibits tumor growth in mice. Disulfiram inhibits growth and angiogenesis in melanomas transplanted in severe combined immunodeficient mice, and these effects are potentiated by Zn2+ supplementation[4]. |
| Cell Assay | The effect of disulfiram (0.15-5.0 μM) or sodium diethyldithiocarbamate (1.0 μM) on proliferation of malignant cell lines is studied in cultures stimulated with 10% FBS. Cell numbers are quantitated 24 to 72 hours later, as outlined below. In some experiments, disulfiram is added immediately after cells are plated. In other experiments, cells are plated and allowed to grow for 24 to 72 hours before fresh medium with disulfiram is added and cell numbers are assayed 24 to 72 hours later. Synergy is studied between disulfiram and N,N′-bis(2-chloroethyl-N-nitrosourea (carmustine, 1.0-1,000 μM) or cisplatin (0.1-100 μg/mL) added to medium. The effect of metal ions on disulfiram is studied with 0.2 to 10 μM Cu2+ (provided as CuSO4), Zn2+ (as ZnCl2), Ag+ (as silver lactate), or Au3+ (as HAuCl4·3H2O) ions added to growth medium, buffered to physiologic pH. To provide a biologically relevant source of copper, medium is supplemented with human ceruloplasmin at doses replicating low and high normal adult serum concentrations (250 and 500 mg/mL). |
| Animal Admin | Adult female CB17-SCID mice are housed in a protected laminar flow facility with access to water and either a standard diet containing 87 ppm zinc or a zinc-supplemented diet containing 1,000 ppm Zn2+ as zinc acetate. Mice are injected s.c. in the right groin with 5×106 cells from a highly aggressive malignant melanoma obtained from a Carolinas Medical Center patient. The frozen tumor is passaged twice in SCID mice to adapt it to in vivo growth before use in these experiments. On the day of tumor injection, all mice began daily administration of drug. Drug is given in a total volume of 0.2 mL by gastric gavage via smooth Teflon-tipped needles inserted transorally into the stomach. Four groups are studied: tumor control (n=10; 0.2 mL olive oil daily; zinc diet of 87 ppm); zinc-supplemented control (n=10; 0.2 mL olive oil daily; zinc diet of 1,000 ppm); disulfiram (n=10; 200 mg/kg/d disulfiram in 0.2 mL olive oil; zinc diet of 87 ppm); and zinc-supplemented diet + disulfiram (n=10; 200 mg/kg/d disulfiram in 0.2 mL olive oil; zinc diet of 1,000 ppm). Mice are examined daily, the tumor is measured in two dimensions, and the tumor volume is estimated using the formula for an elipse. When estimated tumor volume approached 500 mm3 within any animal, all mice are euthanized. Tumors are excised, weighed, fixed in formalin, sectioned, and stained or immunostained for factor VIII. Slides are coded and examined by a blinded observer who identified vessels as deposits of red cells. For each slide, the number of vessels is counted in four different fields representative of the tumor. The average number of vessels per field is averaged per biopsy specimen and used to evaluate tumor vascularity. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 369.0±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 69-71 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C10H20N2S4 |
| Molecular Weight | 296.539 |
| Flash Point | 177.0±23.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 296.050934 |
| PSA | 121.26000 |
| LogP | 3.88 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.620 |
| Storage condition | Store at +4°C |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidants. |
| Water Solubility | 0.02 g/100 mL |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H317-H373-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P280-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R43;R48/22;R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S24-S37-S60-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | JO1225000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 9 |
| HS Code | 29303000 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 29303000 |
|---|

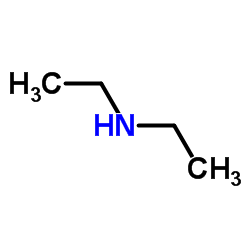
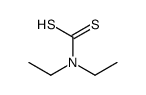
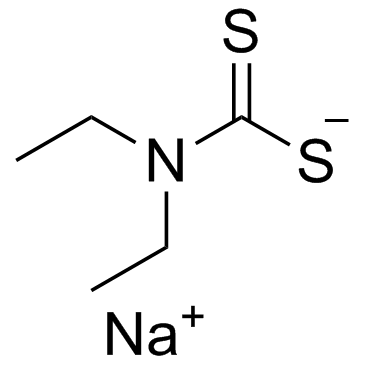
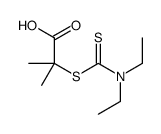

![[(4-methylbenzoyl)amino] N,N-diethylcarbamodithioate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/417/105246-31-9.png)