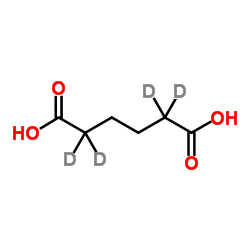
19031-55-1
| Name | 2,2,5,5-tetradeuteriohexanedioic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Hexanedioic-2,2,5,5-d4 acid
Adipic acid-2,2,5,5-d4 2,2,5,5-tetradeuterio-hexanedioic acid (2,2,5,5-H)Hexanedioic acid 2,2,5,5-Tetradeuteroadipinsaeure Hexanedioic-2,2,5,5-d acid |
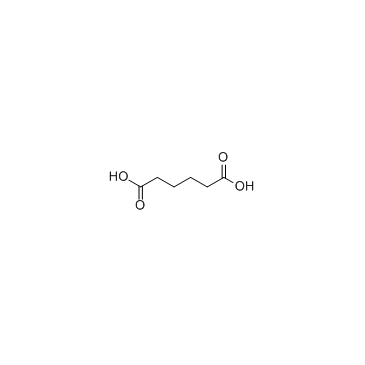
| Description | Adipic acid-d4-1 is the deuterium labeled Adipic acid[1]. Adipic acid is found to be associated with HMG-CoA lyase deficiency, carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency, malonyl-Coa decarboxylase deficiency, and medium Chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, which are inborn errors of metabolism[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 338.5±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 151-154ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H6D4O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 150.166 |
| Flash Point | 196.1±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 150.083023 |
| PSA | 74.60000 |
| LogP | 0.08 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.476 |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36 |
| Safety Phrases | 26 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |
|
~% 
19031-55-1 |
| Literature: Chang,M.; Masek,B.B.; Dougherty,D.A. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1985 , vol. 107, p. 1124 |
|
~% 
19031-55-1 |
| Literature: Nishshanka, Upul; Attygalle, Athula B. Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2008 , vol. 43, # 11 p. 1502 - 1511 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |