β-Methylcrotonyl coenzyme A lithium
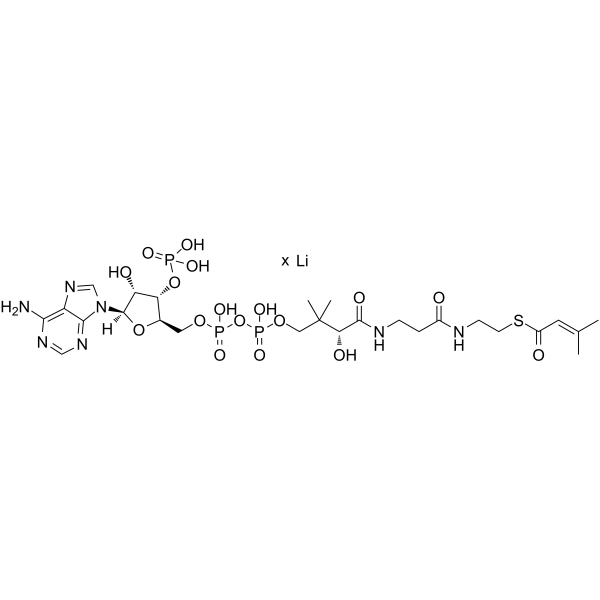
β-Methylcrotonyl coenzyme A lithium structure
|
Common Name | β-Methylcrotonyl coenzyme A lithium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 108347-83-7 | Molecular Weight | 856.57600 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H42LiN7O17P3S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of β-Methylcrotonyl coenzyme A lithiumβ-Methylcrotonyl coenzyme A lithium is an intermediate in leucine metabolism and can be used as a substrate to study the specificity and kinetics of β-methylcrotonyl coenzyme A carboxylase (MCCase)[1]. |
| Name | β-Methylcrotonyl coenzyme A lithium salt |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | β-Methylcrotonyl coenzyme A lithium is an intermediate in leucine metabolism and can be used as a substrate to study the specificity and kinetics of β-methylcrotonyl coenzyme A carboxylase (MCCase)[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | β-Methylcrotonyl coenzyme A carboxylase, which is involved in amino acid metabolism, induces the activity of this enzyme in plant cells due to carbohydrate starvation and can be used as a new biochemical marker of the starvation-triggered autophagy process[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C26H42LiN7O17P3S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 856.57600 |
| Exact Mass | 856.17300 |
| PSA | 425.34000 |
| LogP | 1.89270 |
| Storage condition | 20°C |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-26-36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Regulation of [beta]-Methylcrotonyl-Coenzyme A Carboxylase Activity by Biotinylation of the Apoenzyme.
Plant Physiol. 108 , 1133-1139, (1995) Regulation of the expression of the gene(s) coding for the 78-kD, biotin-containing subunit of [beta]-methylcrotonyl-coenzyme A carboxylase (MCCase) was investigated in different organs of tomato (Lyc... |
|
|
Induction of beta-methylcrotonyl-coenzyme A carboxylase in higher plant cells during carbohydrate starvation: evidence for a role of MCCase in leucine catabolism.
FEBS Lett. 383 , 175-180, (1996) Induction of beta-methylcrotonyl-coenzyme A carboxylase (MCCase) activity was observed during carbohydrate starvation in sycamore cells. In mitochondria isolated from starved cells, we noticed a marke... |
|
|
Essential arginine residues in the active sites of propionyl CoA carboxylase and beta-methylcrotonyl CoA carboxylase.
Enzyme 24 , 302-306, (1979) At least one arginine residue is essential for substrate binding in or near the active sites of propionyl CoA carboxylase (PCC) and beta-methylcrotonyl CoA carboxylase (beta MCC) in cultured human fib... |
| S-[2-[3-[[4-[[[5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-phosphonooxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl]amino]propanoylamino]ethyl] 3-methylbut-2-enethioate,lithium |
| trans-3-Methyl-2-butenoyl Coenzyme A |