Lyso-Globotriaosylceramide (d18:1)
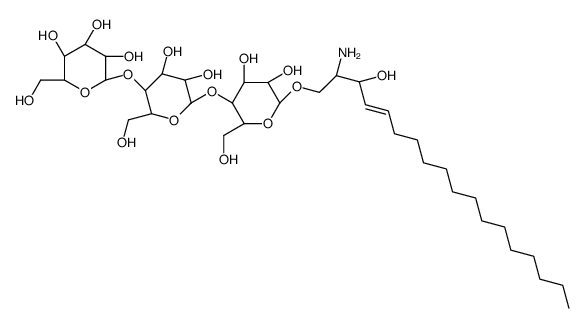
Lyso-Globotriaosylceramide (d18:1) structure
|
Common Name | Lyso-Globotriaosylceramide (d18:1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 126550-86-5 | Molecular Weight | 785.91400 | |
| Density | 1.37g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1005.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C36H67NO17 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 562.1ºC | |
Use of Lyso-Globotriaosylceramide (d18:1)Globotriaosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb3) inhibits the growth of fibroblasts, as well as their differentiation into myofibroblasts, and collagen expression. Globotriaosylsphingosine can be used for Fabry disease research[1]. |
| Name | Globotriaosylsphingosine from porcine blood |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Globotriaosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb3) inhibits the growth of fibroblasts, as well as their differentiation into myofibroblasts, and collagen expression. Globotriaosylsphingosine can be used for Fabry disease research[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.37g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1005.8ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C36H67NO17 |
| Molecular Weight | 785.91400 |
| Flash Point | 562.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 785.44100 |
| PSA | 303.93000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.591 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
LC–MS/MS analysis of plasma lyso-Gb3 in Fabry disease
Clin. Chim. Acta 414 , 273-80, (2012) Background Fabry disease is a complex, multisystemic and clinically heterogeneous disease, with elevated excretion of globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) and globotriaosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb3) accumulating i... |
|
|
A metabolomic study reveals novel plasma lyso-Gb3 analogs as Fabry disease biomarkers.
Curr. Med. Chem. 20(2) , 280-8, (2013) Fabry disease is an X-linked, multisystemic lysosomal storage disorder due to alpha-galactosidase A deficiency. It is characterized by the accumulation of glycosphingolipids, mainly globotriaosylceram... |
|
|
In vivo tumor targeting using a novel intestinal pathogen-based delivery approach.
Cancer Res. 66(14) , 7230-6, (2006) Efficient methods for tumor targeting are eagerly awaited and must satisfy several challenges: molecular specificity, transport through physiologic barriers, and capacity to withstand extracellular or... |
| (2S,3R,4E)-2-Amino-3-hydroxy-4-octadecen-1-yl α-D-galactopyranosyl-(1->4)-β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1->4)-β-D-glucopyranoside |