JTE522
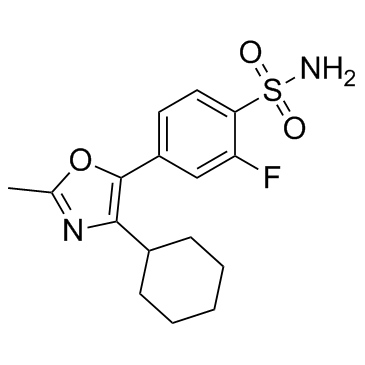
JTE522 structure
|
Common Name | JTE522 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 180200-68-4 | Molecular Weight | 338.39700 | |
| Density | 1.294g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 500.6ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H19FN2O3S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 256.5ºC | |
Use of JTE522JTE522 is a highly selective, time-dependent and irreversible human COX-2 inhibitor with an IC50 of 85 nM in an enzyme assay. |
| Name | tilmacoxib |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | JTE522 is a highly selective, time-dependent and irreversible human COX-2 inhibitor with an IC50 of 85 nM in an enzyme assay. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human COX-2:85 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Inhibitory activity and the mechanism of action of JTE522 (JTE-522), a novel selective cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitor, on human COX-1 and COX-2 are investigated and compared with those of reference compounds. In an enzyme assay, JTE522 inhibits yeast-expressed human recombinant COX-2 with an IC50 of 0.085 μM. In contrast, JTE522 does not inhibit human COX-1 prepared from human platelets at concentrations up to 100 μM. In a cell-based assay, JTE522 diminishes lipopolysaccharide-induced prostaglandin E2 production in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (COX-2) (IC50=15.1 nM). On the other hand, JTE522 is less potent at inhibiting calcium ionophore-induced thromboxane B2 production in washed human platelets (COX-1) (IC50=6.21 μM). JTE522 shows highly selective inhibition of human COX-2, and its activity is more selective than that of other COX-2 inhibitors (NS-398 and SC-58635). Human recombinant COX-2 activity is attenuated by JTE522 in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner[1]. Inhibition of proliferation of gastric epithelial cells by a cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor, JTE522, is also mediated by a PGE2-independent pathway Combination of JTE522 and Arachidonic acid results in a marked retardation of wound healing compared to the control, but JTE522 does not completely suppress the increase in cellular PGE2 content following the addition of arachidonate[2]. |
| In Vivo | The present experiment is designed to assess the potential chemopreventive properties of JTE522 (JTE-522), a new selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, on the induction of 1,2-dimethylhydrazine (DMH)-induced colonic aberrant crypt foci (ACF), a marker of rat colon carcinogenesis. A total of 80 male F344 rats are treated with 3 or 10 mg/kg of body weight JTE522 or vehicle by oral gavage five times weekly from the start of the experiment. One week later, rats receive s.c. injections of saline or 20 mg/kg of body weight DMH once weekly for four successive weeks. At the end of 12 weeks after the start of experiment, all rats are sacrificed and colons are evaluated for ACF. 10 mg/kg JTE522 significantly suppresses the total ACF/colon. No inhibitory effect is observed in the 3 mg/kg JTE522 treatment group. Administration of 10 mg/kg JTE522 significantly suppresses ACF formation with a 30% reduction in total ACF/colon (p<0.01). Furthermore, the data on crypt multiplicity show that 10 mg/kg JTE522 significantly reduces the formation of foci containing 1-3 crypts but not foci containing four crypts or more. Administration of the low dose of JTE522 (3 mg/kg) has no inhibitory effects on either the total ACF or crypt multiplicity[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | Human COX-1 and COX-2 activities are determined. Briefly, human COX-1(0.3 mg protein/assay) or COX-2 (1mg protein/assay) is suspended in 0.2 mL of 100 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) containing hematin (2 μM) and tryptophan (5 mM) as cofactors.The reaction mixture is preincubated with each test drug for 5 min at 24°C. [14C]Arachidonic acid (100,00 dpm,30 μM) is then added to the mixture and incubated for 2 min (COX-1) or 5 min (COX-2) at 24°C. The reaction is stopped by the addition of 400 μL of a stop solution composed of diethyl ether/methanol/1M citric acid (30:4: 1,v/v).After centrifugation of the mixture at 1,700 × g for 5 min at 4°C, 50 μL of the upper phase is applied to a thin-layer chromatography (TLC) plate.TLC is performed at 4°C with a solvent system consisting of diethyl ether/methanol/acetic acid (90:2:0.1,v/v). Enzyme activity is calculated from the percent conversion of Arachidonic acid to PGH2 and its decomposition products,using a BAS2000 system[1]. |
| Cell Assay | JTE522 is resolved with DMSO prior to the experiment and concentrations of 1-100 μM are assessed. Effects of Arachidonic acid are assessed at concentrations of 0, 5 and 20 μg/mL. Further, the combination of JTE522 (100 μM) with Arachidonic acid (20 μg/mL) is assessed in additional experiments. Circular artificial wounds are created after formation of complete monolayer cell sheets. JTE522 and Arachidonic acid are added just after wound formation. The process of epithelial restoration is monitored by measuring the cell-free area using an inverted phase-contrast microscope every 24 h. Changes in the cell-free area during restoration are analyzed quantitatively with an image analyser[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[3] A total of 80 male F344 rats, 5 weeks old, are used. Rats at 6 weeks of age after 1 week of acclimatization are divided randomly into five groups. The rats in groups 1-3 (20 rats each) are injected s.c. with DMH (20 mg/kg body wt) from 1 week after the start of the experiment, once weekly for four successive weeks. Those in groups 4 and 5 (10 rats each) are injected s.c. with 0.9% saline at the same time. Group 2 is treated with JTE522 at a dose of 3 mg/kg body wt by oral gavage, five times weekly from the start of the experiment to the end of the experiment. Groups 3 and 5 are treated with JTE522 at the dose of 10 mg/kg body wt in the same manner as group 2. Groups 1 and 4 are treated with 0.5% CMC alone, without JTE522. Body weight, water and food consumption are measured weekly during the experiment. |
| References |
| Density | 1.294g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 500.6ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C16H19FN2O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 338.39700 |
| Flash Point | 256.5ºC |
| Exact Mass | 338.11000 |
| PSA | 94.57000 |
| LogP | 5.26530 |
| Vapour Pressure | 3.75E-10mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.56 |
|
~84% 
JTE522 CAS#:180200-68-4 |
| Literature: Japan Tobacco Inc. Patent: US6372915 B1, 2002 ; Location in patent: Page column 12 - 13 ; |
|
~% 
JTE522 CAS#:180200-68-4 |
| Literature: Hashimoto, Hiromasa; Imamura, Katsuaki; Haruta, Jun-Ichi; Wakitani, Korekiyo Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2002 , vol. 45, # 7 p. 1511 - 1517 |
| Tilmacoxib |
| JTE-522 |
| 4-(4-cyclohexyl-2-methyl-1,3-oxazol-5-yl)-2-fluorobenzenesulfonamide |
| JTE522 |