Conoidin A
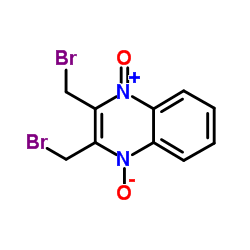
Conoidin A structure
|
Common Name | Conoidin A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 18080-67-6 | Molecular Weight | 347.991 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H8Br2N2O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Conoidin AConoidin A is a cell permeable inhibitor of T. gondii enzyme peroxiredoxin II (TgPrxII) with nematicidal properties. Conoidin A covalently binds to the peroxidatic Cys47 of TgPrxII, irreversibly inhibiting its hyperperoxidation activity with an IC50 of 23 µM. Conoidin A also inhibits hyperoxidation of mammalian PrxI and PrxII (but not PrxIII)[1][2]. Conoidin A has antioxidant, neuroprotective effects and can be used for the research of ischaemic heart disease[3]. |
| Name | 2,3-bis(bromomethyl)-4-oxidoquinoxalin-1-ium 1-oxide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Conoidin A is a cell permeable inhibitor of T. gondii enzyme peroxiredoxin II (TgPrxII) with nematicidal properties. Conoidin A covalently binds to the peroxidatic Cys47 of TgPrxII, irreversibly inhibiting its hyperperoxidation activity with an IC50 of 23 µM. Conoidin A also inhibits hyperoxidation of mammalian PrxI and PrxII (but not PrxIII)[1][2]. Conoidin A has antioxidant, neuroprotective effects and can be used for the research of ischaemic heart disease[3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 23 µM (T. gondii enzyme peroxiredoxin II (TgPrxII))[1] |
| In Vitro | Peroxiredoxins are a widely conserved family of enzymes that function in antioxidant defense and signal transduction. And the changes in PrxII expression are associated with a variety of human diseases, including cancer[1]. Conoidin A binds to the peroxidatic cysteine of TgPrxII, inhibiting its enzymatic activity in vitro. Conoidin A also shown to alkylate or crosslink catalytic cysteines of wild type AcePrx-1 in Ancylostoma ceylanicum and human PrxII and PrxIV with similar efficiency. But it is ineffective to mitochondrial hPrxIII[2]. Conoidin A (5 µM) can inhibit the glucose oxidase-mediated hyperoxidation of mammalian peroxiredoxin I and II[2]. |
| In Vivo | Conoidin A (intraperitoneal injection; 5 mg/kg; for three successive days before MI/R injury) blocks the effect of Luteolin (HY-N0162) on the ST‐segment elevation. Furthermore, an increase in the infarct size presented of the MI/R group can be reduced by Luteolin. But pre‐treatment with conoidin A abolishs the effect of Luteolin. Pre‐treatment with conoidin A also prevents Luteolin-reduced activities of CK‐MB, AST and LDH in vivo[3]. Animal Model: Rat myocardial I/R model[3] Dosage: 5 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; 5 mg/kg; for three successive days before MI/R injury Result: Significantly reversed the antioxidative effect of Luteolin. Impaired the protective effects of luteolin. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C10H8Br2N2O2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 347.991 |
| Exact Mass | 345.895233 |
| PSA | 50.92000 |
| LogP | 3.48660 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|---|
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|
~89% 
Conoidin A CAS#:18080-67-6 |
| Literature: Carmeli, Mira; Rozen, Shlomo Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2006 , vol. 71, # 15 p. 5761 - 5765 |
|
~65% 
Conoidin A CAS#:18080-67-6 |
| Literature: Pearson, Russell J.; Evans, Kathryn M.; Slawin, Alexandra M. Z.; Philp, Douglas; Westwood, Nicholas J. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2005 , vol. 70, # 13 p. 5055 - 5061 |
|
~82% 
Conoidin A CAS#:18080-67-6 |
| Literature: Haddadin, Makhluf J.; Samaha, Mona S.; Hajj-Ubayd, Antoun B. Heterocycles, 1992 , vol. 33, # 2 p. 541 - 544 |
|
~% 
Conoidin A CAS#:18080-67-6 |
| Literature: Pearson, Russell J.; Evans, Kathryn M.; Slawin, Alexandra M. Z.; Philp, Douglas; Westwood, Nicholas J. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2005 , vol. 70, # 13 p. 5055 - 5061 |
|
~% 
Conoidin A CAS#:18080-67-6 |
| Literature: Haddadin, Makhluf J.; Samaha, Mona S.; Hajj-Ubayd, Antoun B. Heterocycles, 1992 , vol. 33, # 2 p. 541 - 544 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
| 2,3-bis(bromomethyl)quinoxaline-1,4-dioxide |
| quinoxaline, 2,3-bis(bromomethyl)-, 1,4-dioxide |
| Quinoxalinium, 2,3-bis(bromomethyl)-1,4-dihydro-4-hydroxy-1-oxo-, inner salt |
| 2,3-Bis-bromomethyl-quinoxaline 1,4-dioxide |
| 2,3-Bis(bromomethyl)-1-oxoquinoxalin-1-ium-4(1H)-olate |
| 2,3-Bis-brommethyl-chinoxalin-1,4-dioxid |


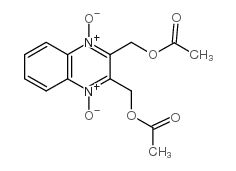 CAS#:10103-89-6
CAS#:10103-89-6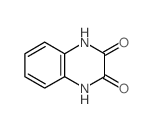 CAS#:15804-19-0
CAS#:15804-19-0 CAS#:17311-31-8
CAS#:17311-31-8