Propachlor
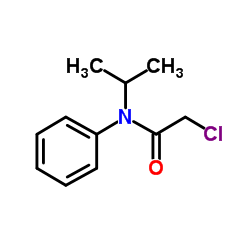
Propachlor structure
|
Common Name | Propachlor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1918-16-7 | Molecular Weight | 211.688 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 290.4±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H14ClNO | Melting Point | 67-76°C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 129.4±22.6 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of PropachlorPropachlor is a specific ALDH1A1 inhibitor. It is sometimes used as an herbicide. |
| Name | propachlor |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 290.4±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 67-76°C |
| Molecular Formula | C11H14ClNO |
| Molecular Weight | 211.688 |
| Flash Point | 129.4±22.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 211.076385 |
| PSA | 20.31000 |
| LogP | 2.28 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.551 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H317-H319-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36;R43;R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S24-S37-S60-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 |
| RTECS | AE1575000 |
| HS Code | 2924299014 |
| HS Code | 2924299014 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299014 2-chloro-n-isopropyl-n-phenylacetamide。supervision conditions:s(import or export registration certificate for pesticides)。VAT:17.0%。tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tarrif:6.5%。general tariff:30.0% |
|
Glutathione-dependent cytotoxicity of the chloroacetanilide herbicides alachlor, metolachlor, and propachlor in rat and human hepatoma-derived cultured cells.
Cell Biol. Toxicol. 15(5) , 325-32, (1999) Alachlor, metolachlor, and propachlor are widely used chloroacetanilide herbicides. Their cytotoxicity in rat (Fa32) and human (Hep G2) hepatoma-derived cells was investigated, in connection with thei... |
|
|
Kinetics and mechanism of propachlor reductive transformation through nucleophilic substitution by dithionite
Chemosphere 85(9) , 1438-43, (2011) Highlights ► The reductive dechlorination of propachlor was efficiently achieved by dithionite. ► The transformation of propachlor initiated by dithionite follows second-order kinetics. ► Dechlorinati... |
|
|
Characterization of glutathione conjugates of chloroacetanilide pesticides using ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography/ion trap mass spectrometry.
Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 21(24) , 4017-22, (2007) Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) isolated from maize were used to catalyze the conjugation of glutathione (GSH) with chloroacetanilide herbicides, producing stable conjugates that were structurally c... |
| 2-Chloro-N-isopropylacetanilide |
| Satecid |
| N-isopropyl-2-chloroacetanilide |
| 2-Chloro-N-isopropyl-N-phenyl-acetamide |
| Niticid |
| N-isopropyl-N-phenyl-chloroacetamide |
| 2-Chloro-N-isopropyl-N-phenylacetamide |
| Prolex |
| Propachlore |
| 2-Chloro-N-(1-methylethyl)-N-phenylacetamide (9CI) |
| Nitacid |
| α-chloro-N-isopropylacetanilide |
| MFCD00078731 |
| EINECS 217-638-2 |
| Bexton |
| 2-chloro-N-(1-methylethyl)-N-phenylacetamide |
| 2-chloro-N-phenyl-N-(propan-2-yl)acetamide |
| n-isopropyl-a-chloroacetanilide |
| Bexton 4L |
| 2-chloro-N-phenyl-N-propan-2-ylacetamide |
| Acetamide, 2-chloro-N-(1-methylethyl)-N-phenyl- |
| Ramrod |
| Propachlor |
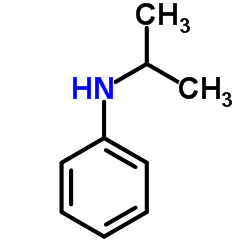 CAS#:768-52-5
CAS#:768-52-5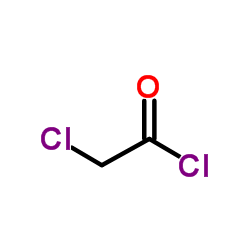 CAS#:79-04-9
CAS#:79-04-9 CAS#:10487-31-7
CAS#:10487-31-7