PR-619
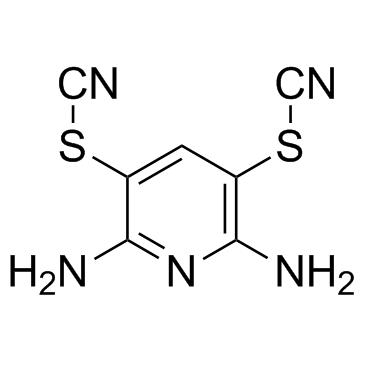
PR-619 structure
|
Common Name | PR-619 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2645-32-1 | Molecular Weight | 223.278 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 406.0±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H5N5S2 | Melting Point | 210℃ | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 199.3±28.7 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of PR-619PR-619 is a broad-range DUB inhibitor with EC50 of 3.93, 4.9, 6.86, 7.2, and 8.61 μM for USP4, USP8, USP7, USP2, and USP5, respectively. |
| Name | (2,6-diamino-5-thiocyanatopyridin-3-yl) thiocyanate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | PR-619 is a broad-range DUB inhibitor with EC50 of 3.93, 4.9, 6.86, 7.2, and 8.61 μM for USP4, USP8, USP7, USP2, and USP5, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
EC50: 3.93 μM (USP4), 4.9 μM (USP8), 6.86 μM (USP7), 7.2 μM (USP2), 8.61 μM (USP5)[1] |
| In Vitro | PR-619, a deubiquitylase inhibitor, prevents degradation, indicating KCa3.1 is targeted for degradation by ubiquitylation. In PR-619 treated cells, channel degradation is significantly inhibited with 87±1% of KCa3.1 still remaining after 24 hrs (n=3; P<0.05)[2]. Cell viability is determined by MTT assay and revealed that PR-619 exerted concentration-dependent cytotoxicity in a very narrow concentration range of 7-10 μM[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | Recombinant enzymes in 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 2 mM CaCl2 and 2 mM β-mercaptoethanol (DUB assay buffer) are preincubated with single doses or dose ranges of PR-619 or P22077 for 30 minutes in a 96 well plate before the addition of Ub-PLA2 and NBD C6-HPC. The liberation of a fluorescent product within the linear range of the assay is monitored at room temperature using a Perkin Elmer Envision fluorescence plate reader. Vehicle (2%(v/v) DMSO) and 10mM N-ethylmaleimide are included as controls. Where ≥60% inhibition is observed, EC50 values are determined using a sigmoidal dose response equation. A similar assay protocol is used to measure other in vitro enzyme assay activities[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Growth inhibition is determined with the exception that HCT-116 or HEK293T cells maintained in DMEM supplemented with 10% (v/v) FBS, 1% (v/v) penicillin/streptomycin and 2 mM L-glutamine are exposed to dose ranges of PR-619 (1, 5, 10, 20, and 50 μM) or P22077 for 72 hours[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 406.0±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 210℃ |
| Molecular Formula | C7H5N5S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 223.278 |
| Flash Point | 199.3±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 222.998642 |
| PSA | 163.84000 |
| LogP | 2.05 |
| Appearance of Characters | white to beige |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.764 |
| Storage condition | ?20°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: soluble5mg/mL (clear solution) |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H317-H318-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 22-37/38-41-43 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
|
Development of two novel high-throughput assays to quantify ubiquitylated proteins in cell lysates: application to screening of new anti-malarials.
Malaria Journal 14 , 200, (2015) The ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS) is one of the main proteolytical pathways in eukaryotic cells and plays an essential role in key cellular processes such as cell cycle, stress response, signal tr... |
|
|
Inflammasomes-dependent regulation of IL-1β secretion induced by the virulent Mycobacterium bovis Beijing strain in THP-1 macrophages.
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 108 , 163-71, (2015) Mycobacterium bovis is the causative agent of tuberculosis in cattle. Infection of macrophages with M. bovis leads to the activation of the "nucleotide binding and oligomerization, leucine-rich repeat... |
|
|
Screening of DUB activity and specificity by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.
Nat. Commun. 5 , 4763, (2014) Deubiquitylases (DUBs) are key regulators of the ubiquitin system which cleave ubiquitin moieties from proteins and polyubiquitin chains. Several DUBs have been implicated in various diseases and are ... |
| Thiocyanic acid, 2,6-diamino-3,5-pyridinediyl ester |
| 2,6-Diaminopyridine-3,5-bis(thiocyanate) |
| 2,6-diamino-5-(cyanothio)pyridin-3-yl thiocyanate |
| Thiocyanic acid,2,6-diamino-3,5-pyridinediyl ester |
| 3,5-bis-thiocyanato-pyridine-2,6-diamine |
| HMS1440E01 |
| 2,6-Diamino-3,5-dithiocyanato-pyridin |
| 2,6-diamino-3,5-bis(thiocyanato)pyridine |
| QC-8206 |
| 2,6-Diamino-3,5-pyridinediyl bis(thiocyanate) |
| 3,5-dithiocyanatopyridine-2,6-diamine |
| PR-619 |
 CAS#:70999-08-5
CAS#:70999-08-5
