L-Glyceric acid
Modify Date: 2024-01-07 15:56:26
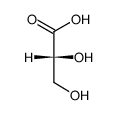
L-Glyceric acid structure
|
Common Name | L-Glyceric acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 28305-26-2 | Molecular Weight | 106.07700 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of L-Glyceric acidL-Glyceric acid is a mainly urinary metabolite accumulating in rare inherited metabolic disease L-glyceric aciduria. L-Glyceric acid can be used to diagnose primary hyperoxaluria type 2 (PH2). L-Glyceric acid excretion to distinguish PH1 from PH2[1][2]. |
| Name | D-glyceric acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Glyceric acid is a mainly urinary metabolite accumulating in rare inherited metabolic disease L-glyceric aciduria. L-Glyceric acid can be used to diagnose primary hyperoxaluria type 2 (PH2). L-Glyceric acid excretion to distinguish PH1 from PH2[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Primary hyperoxaluria type 2 (PH2), also called L-glyceric aciduria. The metabolic defect is due to deficiencies of D-glycerate dehydrogenase and glyoxylate reductase, leading to excretion of L-Glyceric acid, and L-Glyceric acid is the cornerstone for the diagnosis of PH2[1][2]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6O4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 106.07700 |
| Exact Mass | 106.02700 |
| PSA | 77.76000 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| (2s)-2,3-dihydroxypropanoic acid |
| l-glyceric acid |