POLY-L-ISOLEUCINE
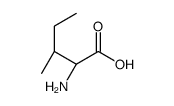
POLY-L-ISOLEUCINE structure
|
Common Name | POLY-L-ISOLEUCINE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 34464-35-2 | Molecular Weight | 131.17300 | |
| Density | 1.035g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 225.8ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H13NO2 | Melting Point | 284ºC (decomposes) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 90.3ºC | |
| Name | L-Isoleucine |
|---|
| Density | 1.035g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 225.8ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 284ºC (decomposes) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H13NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 131.17300 |
| Flash Point | 90.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 131.09500 |
| PSA | 63.32000 |
| LogP | 1.14470 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Direct evidence of the amino acid side chain and backbone contributions to protein anharmonicity.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(4) , 1371-6, (2010) Elastic incoherent neutron scattering has been used to study the temperature dependence of the mean-square displacements of nonexchangeable hydrogen atoms in powders of a series of homomeric polypepti... |
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum stress caused by aggregate-prone proteins containing homopolymeric amino acids.
FEBS J. 274(21) , 5619-27, (2007) Many human proteins have homopolymeric amino acid (HPAA) tracts, but their physiological functions or cellular effects are not well understood. Previously, we expressed 20 HPAAs in mammalian cells and... |
|
|
A solvent model for simulations of peptides in bilayers. I. Membrane-promoting alpha-helix formation.
Biophys. J. 76(5) , 2448-59, (1999) We describe an efficient solvation model for proteins. In this model atomic solvation parameters imitating the hydrocarbon core of a membrane, water, and weak polar solvent (octanol) were developed. A... |