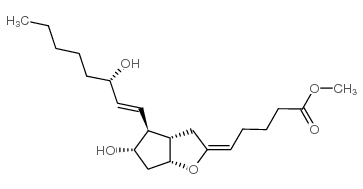
Epoprostenol

Epoprostenol structure
|
Common Name | Epoprostenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 35121-78-9 | Molecular Weight | 374.44700 | |
| Density | 1.221g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 530.2ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H31NaO5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 182.1ºC | |
Use of EpoprostenolEpoprostenol (Prostaglandin I2), the synthetic form of the natural prostaglandin derivative Prostacyclin (Prostaglandin I2), is registered worldwide for the treatment of Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH. Epoprostenol is used in pulmonary hypertension and transplantation as a potent inhibitor of platelet aggregation[1]. |
| Name | prostaglandin I2 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Epoprostenol (Prostaglandin I2), the synthetic form of the natural prostaglandin derivative Prostacyclin (Prostaglandin I2), is registered worldwide for the treatment of Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH. Epoprostenol is used in pulmonary hypertension and transplantation as a potent inhibitor of platelet aggregation[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.221g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 530.2ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H31NaO5 |
| Molecular Weight | 374.44700 |
| Flash Point | 182.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 374.20700 |
| PSA | 89.82000 |
| LogP | 2.07380 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.611 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
|---|---|
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22 |
| Safety Phrases | S22;S26;S36 |
|
~% 
Epoprostenol CAS#:35121-78-9 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron Letters, , vol. 24, # 11 p. 1187 - 1188 |
|
~% 
Epoprostenol CAS#:35121-78-9 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron Letters, , vol. 24, # 11 p. 1187 - 1188 |
|
~% 
Epoprostenol CAS#:35121-78-9 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron Letters, , vol. 24, # 11 p. 1187 - 1188 |
| PGX |
| Epoprostenol |
| MFCD00135629 |
| Prostaglandin l2 |
| prostacyclin |
| Vasocyclin |
| PGl2 |
| ProstaglandinI |
| PGX(prostaglandin) |
| Cyclo-Prostin |
| EINECS 263-273-7 |
| Prostaglandin X |
![methyl (5Z,13E,15S)-11alpha,15-bis[[(tert-butyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]-6,9alpha-epoxyprosta-5,13-dien-1-oate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/126/78824-82-5.png)