Perfluoroheptanoic acid
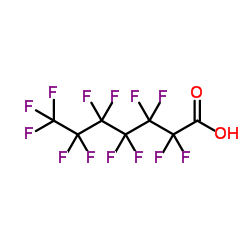
Perfluoroheptanoic acid structure
|
Common Name | Perfluoroheptanoic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 375-85-9 | Molecular Weight | 364.061 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 175.8±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7HF13O2 | Melting Point | ~30 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 51.3±25.9 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | perfluoroheptanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 175.8±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | ~30 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C7HF13O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 364.061 |
| Flash Point | 51.3±25.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 363.976898 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 6.86 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.5±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.289 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong bases. |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H314 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | C:Corrosive; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R34 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 3261 8/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| HS Code | 2915900090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2915900090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2915900090 other saturated acyclic monocarboxylic acids and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:5.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Antibiotic delivery by liposomes from prokaryotic microorganisms: Similia cum similis works better.
Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 94 , 411-8, (2015) To date the effectiveness of antibiotics is undermined by microbial resistance, threatening public health worldwide. Enhancing the efficacy of the current antibiotic arsenal is an alternative strategy... |
|
|
Occurrence of perfluorinated alkyl substances in sediment from estuarine and coastal areas of the East China Sea.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 22(3) , 1662-9, (2015) Perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) have drawn much attention due to their environmental persistence, ubiquitous existence, and bioaccumulation potential. The occurrence and spatial variation of PF... |
|
|
Sources and fate of perfluorinated compounds in the aqueous environment and in drinking water of a highly urbanized and industrialized area in Italy.
J. Hazard. Mater. 282 , 51-60, (2014) Perfluorinated substances are listed among emerging contaminants because they are globally distributed, environmentally persistent, bioaccumulative and potentially harmful. In a three-year monitoring ... |
| EINECS 206-798-9 |
| Perfluoroheptanoic acid |
| Tridecafluoroheptanoic acid |
| PFHPA |
| Heptanoic acid, 2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,7-tridecafluoro- |
| MFCD00039604 |
| 2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,7-tridecafluoroheptanoic acid |
 CAS#:559-14-8
CAS#:559-14-8 CAS#:355-43-1
CAS#:355-43-1 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9 CAS#:375-83-7
CAS#:375-83-7 CAS#:335-58-0
CAS#:335-58-0 CAS#:20109-59-5
CAS#:20109-59-5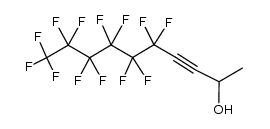 CAS#:106993-79-7
CAS#:106993-79-7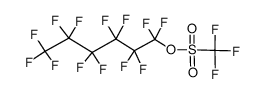 CAS#:78522-65-3
CAS#:78522-65-3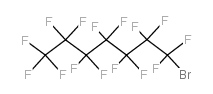 CAS#:375-88-2
CAS#:375-88-2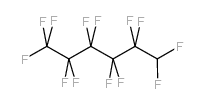 CAS#:355-37-3
CAS#:355-37-3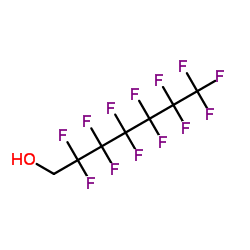 CAS#:375-82-6
CAS#:375-82-6 CAS#:375-84-8
CAS#:375-84-8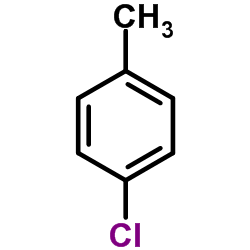 CAS#:106-43-4
CAS#:106-43-4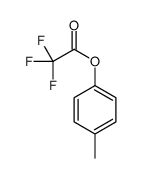 CAS#:1813-29-2
CAS#:1813-29-2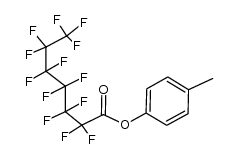 CAS#:102607-12-5
CAS#:102607-12-5 CAS#:2358-22-7
CAS#:2358-22-7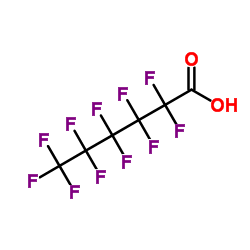 CAS#:307-24-4
CAS#:307-24-4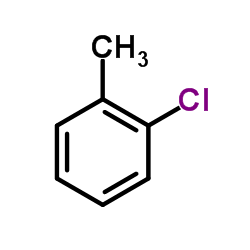 CAS#:95-49-8
CAS#:95-49-8
