Fasentin
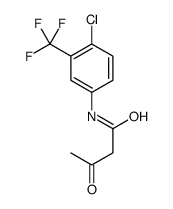
Fasentin structure
|
Common Name | Fasentin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 392721-37-8 | Molecular Weight | 279.64300 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H9ClF3NO2 | Melting Point | 141.7 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of FasentinFasentin, a potent glucose uptake inhibitor, inhibits GLUT-1/GLUT-4 transporters. Fasentin preferentially inhibits GLUT4 (IC50=68 μM) over GLUT1. Fasentin is a death receptor stimuli (FAS) sensitizer and sensitizes cells to FAS-induced cell death. Fasentin is also a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) apoptosis-inducing ligand sensitizer. Fasentin blocks glucose uptake in cancer cell lines and has anti-angiogenic activity[1][2][3]. |
| Name | N-[4-Chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3-oxobutanamide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Fasentin, a potent glucose uptake inhibitor, inhibits GLUT-1/GLUT-4 transporters. Fasentin preferentially inhibits GLUT4 (IC50=68 μM) over GLUT1. Fasentin is a death receptor stimuli (FAS) sensitizer and sensitizes cells to FAS-induced cell death. Fasentin is also a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) apoptosis-inducing ligand sensitizer. Fasentin blocks glucose uptake in cancer cell lines and has anti-angiogenic activity[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
GLUT4:68 μM (IC50) GLUT1 |
| In Vitro | Fasentin (0.1-1000 μM; 72 hours) inhibits endothelial, tumour and fibroblast cell growth without inducing cell death[1]. Fasentin (25-100 μM; 16-24 hours) induces a cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase and reduces the cell number in S phase in a dose-dependent manner[1]. Fasentin (50 μM; 16 hours) alters expression of genes associated with glucose deprivation such as AspSyn and PCK-2[2]. Fasentin (15, 30, 80 μM; pretreatment 1 hour) induces glucose deprivation, partially blocks glucose uptake in PPC-1, DU145, and U937 cells[2]. Fasentin (100 μM; 16 hours) does not affect the migratory capability of endothelial cells[1]. Fasentin (25-100 μM; 16 hours) lowers levels of phospho-ERK in HMECs, indicating a partial inhibition on the ERK signalling pathway, even though the effect is not statistically significant. Fasentin does not inhibit the tyrosine kinase activity of VEGFR2[1]. Fasentin interacts with a unique site in the intracellular channel of GLUT1[3]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: Three types of endothelial cells ECs (HMEC, human microvascular endothelial cells; HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; and BAEC, bovine aortic endothelial cells), three human tumour cell lines (MDA-MB-231 and MCF7 breast carcinoma cells, and HeLa cervix adenocarcinoma cells), and human gingival fibroblasts (HGF) Concentration: 0.1, 1, 10, 100, 1000 μM Incubation Time: 72 hours Result: Inhibited endothelial, tumour and fibroblast cell growth (IC50=26.3-111.2 μM) without inducing cell death. Cell Cycle Analysis[1] Cell Line: HMECs Concentration: 25, 50, 100 μM Incubation Time: 16, 24 hours Result: Induced a cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase and reduced the cell number in S phase in a dose-dependent manner. Did not increase the subG1 population. RT-PCR[2] Cell Line: PPC-1 cells[2] Concentration: 50 μM Incubation Time: 16 hours Result: Altered expression of genes associated with glucose deprivation such as AspSyn and PCK-2 not FLIP mRNA expression. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 141.7 °C |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C11H9ClF3NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 279.64300 |
| Exact Mass | 279.02700 |
| PSA | 49.66000 |
| LogP | 3.92590 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| HS Code | 2924299090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924299090. other cyclic amides (including cyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Ghrelin promotes oral tumor cell proliferation by modifying GLUT1 expression.
Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 73 , 1287-99, (2016) In our study, ghrelin was investigated with respect to its capacity on proliferative effects and molecular correlations on oral tumor cells. The presence of all molecular components of the ghrelin sys... |
| N-(4-Chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3-oxobutanamide |
| Glucose Transporter Inhibitor |
| Fasentin |