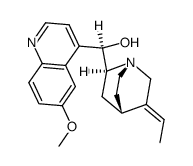
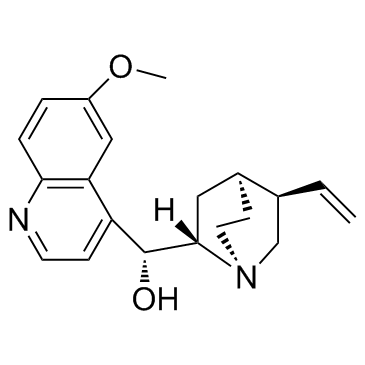
dihydroquinine
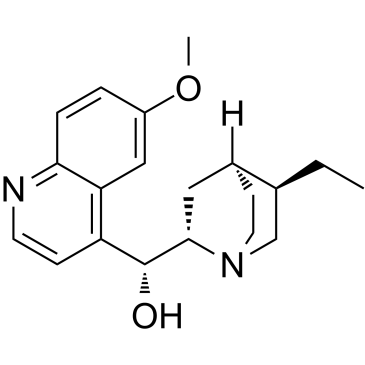
dihydroquinine structure
|
Common Name | dihydroquinine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 522-66-7 | Molecular Weight | 326.433 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 498.4±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H26N2O2 | Melting Point | 168-176ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 255.2±24.6 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of dihydroquinineHydroquinone is a inhibitor of melanin synthesis, serves as a skin whitener and is usually available in cosmetics or on prescription[1].Hydroquinone can be used in the preparation of oxidized light-emitting materials such as lucigenin by inducing the production of hydrogen peroxide in the presence of basic compounds.Hydroquinone (HQ) is the most abundant quinine present in cigarette tar it can enter the circulation via the lungs and can interact with cellular targets throughout the body, hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic properties has been reported[1]. |
| Name | hydroquinine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Hydroquinone is a inhibitor of melanin synthesis, serves as a skin whitener and is usually available in cosmetics or on prescription[1].Hydroquinone can be used in the preparation of oxidized light-emitting materials such as lucigenin by inducing the production of hydrogen peroxide in the presence of basic compounds.Hydroquinone (HQ) is the most abundant quinine present in cigarette tar it can enter the circulation via the lungs and can interact with cellular targets throughout the body, hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic properties has been reported[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 498.4±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 168-176ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C20H26N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 326.433 |
| Flash Point | 255.2±24.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 326.199432 |
| PSA | 45.59000 |
| LogP | 3.77 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.626 |
| Storage condition | 2~8°C |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36 |
| RIDADR | UN 1544 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|
~% 
dihydroquinine CAS#:522-66-7 |
| Literature: Hoffmann-La Roche Inc. Patent: US3931192 A1, 1976 ; |
|
~% 
dihydroquinine CAS#:522-66-7 |
| Literature: Boehringer and Soehne Patent: DE306939 ; Fortschr. Teerfarbenfabr. Verw. Industriezweige, vol. 13, p. 839,840 Full Text Show Details Boehringer and Soehne Patent: DE307894 ; |
|
~% 
dihydroquinine CAS#:522-66-7 |
| Literature: Paal; Amberger Patent: DE346949 ; Fortschr. Teerfarbenfabr. Verw. Industriezweige, vol. 14, p. 1468 |
|
~% 
dihydroquinine CAS#:522-66-7 |
| Literature: Giemsa; Bonath Chemische Berichte, 1925 , vol. 58, p. 95 Full Text Show Details Giemsa; Halberkann Chemische Berichte, 1918 , vol. 51, p. 1330 |
|
~% 
dihydroquinine CAS#:522-66-7 |
| Literature: Giemsa; Bonath Chemische Berichte, 1925 , vol. 58, p. 95 Full Text Show Details Giemsa; Halberkann Chemische Berichte, 1918 , vol. 51, p. 1330 |
|
~% 
dihydroquinine CAS#:522-66-7 |
| Literature: Giemsa; Halberkann Chemische Berichte, 1918 , vol. 51, p. 1330 |
|
~% 
dihydroquinine CAS#:522-66-7 |
| Literature: Henry et al. Journal of the Chemical Society, 1937 , p. 592,600 Journal of the Chemical Society, 1935 , p. 966,967 |
|
~% 
dihydroquinine CAS#:522-66-7 |
| Literature: Henry et al. Journal of the Chemical Society, 1937 , p. 592,600 Journal of the Chemical Society, 1935 , p. 966,967 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Mutation in the Plasmodium falciparum CRT protein determines the stereospecific activity of antimalarial cinchona alkaloids.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 56(10) , 5356-64, (2012) The Cinchona alkaloids are quinoline aminoalcohols that occur as diastereomer pairs, typified by (-)-quinine and (+)-quinidine. The potency of (+)-isomers is greater than the (-)-isomers in vitro and ... |
|
|
Modified asymmetric Strecker reaction of aldehyde with secondary amine: a protocol for the synthesis of S-clopidogrel (an antiplatelet agent).
J. Org. Chem. 77(16) , 7076-80, (2012) A first approach for catalytic asymmetric Strecker reaction of aldehydes with a secondary amine in the presence of sodium fluoride using hydroquinine as chiral catalyst was developed. The catalytic sy... |
|
|
Calculation of standard electrode potential of half reaction for benzoquinone and hydroquinone.
Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 65(2) , 333-9, (2006) Geometric parameters, the vibrational frequencies and thermochemical values of benzoquinone and hydroquinone were computed using ab initio molecular orbital calculations (HF) and density function theo... |
| Cinchonan-9-ol, 10,11-dihydro-6'-methoxy-, (8α,9R)- |
| (1R)-((2S,4S,5R)-5-Ethylquinuclidin-2-yl)(6-methoxyquinolin-4-yl)methanol |
| (8α,9R)-6'-Methoxy-10,11-dihydrocinchonan-9-ol |
| Quinine,10,11-dihydro |
| 10,11-Dihydroquinine |
| HYDROQUININE |
| (8a,9R)-10,11-Dihydro-6'-methoxycinchonan-9-ol |
| Hydroquinine,Dihydroquinine |
| (-)-Dihydroquinine |
| dihydroquinine |
| dihydro quinine |

![(R)-[(2S,4S,5Z)-5-ethylidene-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-2-yl]-(6-methoxyquinolin-4-yl)methanol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/487/16934-07-9.png)