Thiomersal
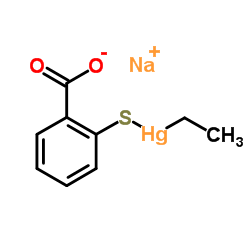
Thiomersal structure
|
Common Name | Thiomersal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 54-64-8 | Molecular Weight | 404.811 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 298.6ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H9HgNaO2S | Melting Point | 234-237 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 250 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of ThiomersalThimerosal, a mercury-containing vaccine preservative, is a suspected factor in the etiology of neurodevelopmental disorders. |
| Name | thimerosal |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Thimerosal, a mercury-containing vaccine preservative, is a suspected factor in the etiology of neurodevelopmental disorders. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | The Thimerosal (THIM) administration increases μ-opioid receptors (MORs) density in the periaqueductal gray (PAG) in a dose-dependent manner. Treatment with higher doses of Thimerosal statistically significantly increases MOR density in the dorsomedial periaqueductal gray (DMPAG) and lateral periaqueductal gray (LPAG) regions. At the dose 3,000 μg Hg/kg, Thimerosal also augments MOR density in the caudate putamen (CPU). In contrast, the administration of Thimerosal at both higher doses decreases MOR density in the dentate gyrus (DG)[1]. Thimerosal administration (4 injections, i.m., 240 μg Hg/kg on postnatal days 7, 9, 11, 15) induces lasting changes in amino acid overflow: an increase of glutamate and aspartate accompanied by a decrease of glycine and alanine; measured 10 to 14 weeks after the injections. Four injections of Thimerosal at a dose of 12.5 μg Hg/kg do not alter glutamate and aspartate concentrations at microdialysis time. Application of Thimerosal to the prefrontal cortex (PFC) in perfusion fluid evokes a rapid increase of glutamate overflow. Coadministration of the neurosteroid, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS; 80 mg/kg; i.p.) prevents the Thimerosal effect on glutamate and aspartate; the steroid alone has no influence on these amino acids. Coapplication of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS) with Thimerosal in perfusion fluid also blocks the acute action of Thimerosal on glutamate[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Male rats are used in this study. On the 20th postnatal week, the animals are euthanized by pentobarbital overdosing, and then decapitated. The rats treated with two higher doses of Thimerosal (THIM) (1,440 and 3,000 μg Hg/kg) are from the original litters, which are used for different behavioral and pathological tests, but are experimentally naïve. A separate group of experimentally naïve rats, treated with two lower doses of Thimerosal, 12 and 240 μg Hg/kg (4 litters per each drug-treatment) is sacrificed on the 8th postnatal week according to the same procedure. Each experimental group is composed of 5 animals, with 2 at the most coming from the same litter[1]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 298.6ºC at 760mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 234-237 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H9HgNaO2S |
| Molecular Weight | 404.811 |
| Flash Point | 250 °C |
| Exact Mass | 405.992706 |
| PSA | 65.43000 |
| LogP | 1.57790 |
| Stability | Stable. May degrade in sunlight. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents, iodine, heavy metal salts. |
| Water Solubility | 1 G/ML (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H300 + H310 + H330-H373-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | Missing Phrase - N15.00950417-P260-P262-P280-P302 + P352 + P310-P304 + P340 + P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+:Verytoxic;N:Dangerous for the environment; |
| Risk Phrases | R26/27/28;R33;R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S13-S28-S36-S45-S60-S61-S28A |
| RIDADR | UN 2025 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | OV8400000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 29310095 |
| HS Code | 29310095 |
|---|
|
Safety review: squalene and thimerosal in vaccines.
Therapie. 65(6) , 533-41, (2010) Few studies show the reluctance of the people to get vaccinated against A (H1N1) influenza for fear of side effects of squalene (MF59, AS03, AF03) and thimerosal. The aim of this paper is to assess th... |
|
|
A transcriptome-based classifier to identify developmental toxicants by stem cell testing: design, validation and optimization for histone deacetylase inhibitors.
Arch. Toxicol. 89 , 1599-618, (2015) Test systems to identify developmental toxicants are urgently needed. A combination of human stem cell technology and transcriptome analysis was to provide a proof of concept that toxicants with a rel... |
|
|
Autophagy-inducing peptides from mammalian VSV and fish VHSV rhabdoviral G glycoproteins (G) as models for the development of new therapeutic molecules.
Autophagy 10(9) , 1666-80, (2014) It has not been elucidated whether or not autophagy is induced by rhabdoviral G glycoproteins (G) in vertebrate organisms for which rhabdovirus infection is lethal. Our work provides the first evidenc... |
| sodium ethyl[2-(mercapto-kS)benzoato(2-)]mercurate(1-) |
| Thimersalate |
| MFCD00013062 |
| Thiomersalate |
| sodium,(2-carboxylatophenyl)sulfanyl-ethylmercury |
| Thimerosalate |
| Merthiolate sodium |
| Thiomersal |
| Thimerosal |
| MERTHIOLATE |
| sodium salt of (2-carboxyphenylthio)ethylmercury |
| mercurate(1-), ethyl[2-(mercapto-κS)benzoato(2-)]-, sodium |
| Mercurate(1-), ethyl[2-(mercapto-κS)benzoato(2-)]-, sodium (1:1) |
| Sodium ethyl[2-(sulfanyl-κS)benzoato(2-)]mercurate(1-) |
| sodium ethyl[2-(mercapto-κS)benzoato(2)-κO]mercurate(1) |
| Thimerosalum |
| EINECS 200-210-4 |
| Mercurothiolate |
| Sodium merthiolate |
| sodium 2-(ethylmercuriothio)benzoate |
| Natriumethyl[2-(sulfanyl-κS)benzoeato(2-)]mercurate(1-) |
| Sodium ethylmercurithiosalicylate |