L-Aspartic acid
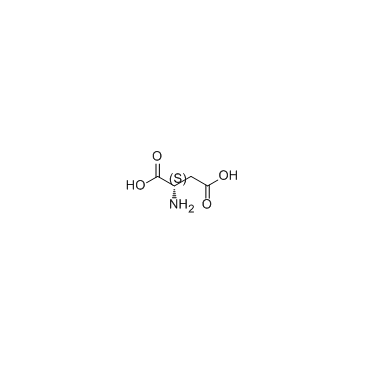
L-Aspartic acid structure
|
Common Name | L-Aspartic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 56-84-8 | Molecular Weight | 133.103 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 264.1±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H7NO4 | Melting Point | >300 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 113.5±24.6 °C | |
Use of L-Aspartic acidL-Aspartic acid is is an amino acid, shown to be a suitable prodrug for colon-specific drug deliverly. |
| Name | L-aspartic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Aspartic acid is is an amino acid, shown to be a suitable prodrug for colon-specific drug deliverly. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vivo | L-Aspartic acid is shown to be a suitable prodrug for colon-specific drug deliverly[1]. L-[3H]Asp remaining in the brain at 5 min is increased by 206 and 178% by preadministration of 100 mM L-Aspartic acid and 100 mM L-Glu, respectively, whereas 100 mM D-Asp does not affect L-[3H]Asp efflux transport. That value for L-[3H]Glu at 20 min is increased by 145 and 156% by coadministration with 100 mM L-Aspartic acid and 100 mM L-Glu, respectively, but not by D-Asp. It is interesting that the apparent efflux rate of L-Aspartic acid across the BBB is sevenfold faster than that of L-Glu[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 264.1±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >300 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C4H7NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 133.103 |
| Flash Point | 113.5±24.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 133.037506 |
| PSA | 100.62000 |
| LogP | -0.67 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.531 |
| Water Solubility | 5 g/L (25 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant;Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R36 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S24/25-S22 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | CI9098500 |
| HS Code | 29224995 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Rad23 interaction with the proteasome is regulated by phosphorylation of its ubiquitin-like (UbL) domain.
J. Mol. Biol. 426(24) , 4049-60, (2014) Rad23 was identified as a DNA repair protein, although a role in protein degradation has been described. The protein degradation function of Rad23 contributes to cell cycle progression, stress respons... |
|
|
Mechanism of chemical activation of sodium chloride in the presence of amino acids.
Food Chem. 166 , 301-8, (2014) Sodium chloride has been shown to promote chlorination of glycerol during thermal processing. However, the detailed mechanism of this reaction is not well understood. Preliminary experiments have indi... |
|
|
EAAT2 (GLT-1; slc1a2) glutamate transporters reconstituted in liposomes argues against heteroexchange being substantially faster than net uptake.
J. Neurosci. 34(40) , 13472-85, (2014) The EAAT2 glutamate transporter, accounts for >90% of hippocampal glutamate uptake. Although EAAT2 is predominantly expressed in astrocytes, ∼10% of EAAT2 molecules are found in axon terminals. Despit... |
| asparagic acid |
| 1-amino-1,2-carboxyethane |
| δ-aspartic acid |
| d-Asp |
| QVYZ1VQ &&D or R Form |
| (-)-Aspartic acid |
| (2R)-2-Aminosuccinic acid |
| MFCD00002616 |
| (2R)-2-aminobutanedioic acid |
| hydrogen D-aspartate |
| L-Asparticacid |
| (R)-(−)-Aminosuccinic acid |
| D-(-)-Aspartic acid |
| Acide (2R)-2-aminosuccinique |
| L-Aspartic acid |
| aspartic acid D-form |
| Aspartic acid, D- |
| D-Aspartic acid |
| H-D-Asp-OH |
| EINECS 200-291-6 |
| H-Asp-OH |
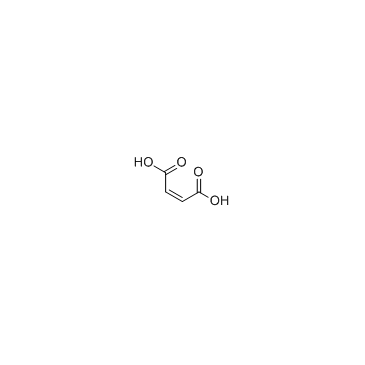 CAS#:110-16-7
CAS#:110-16-7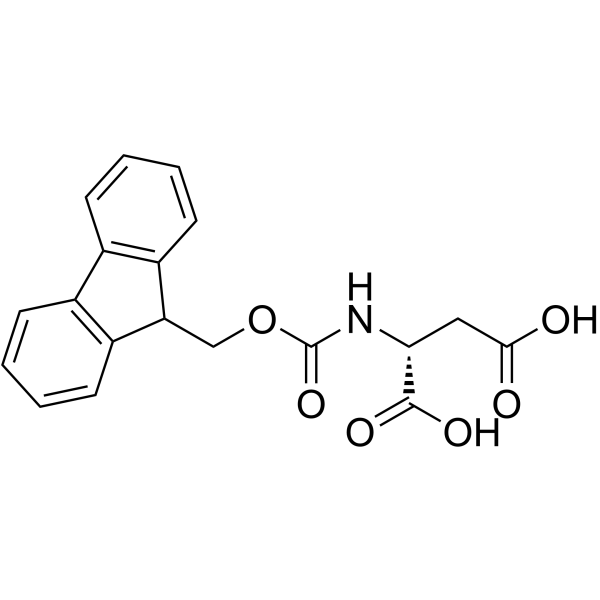 CAS#:136083-57-3
CAS#:136083-57-3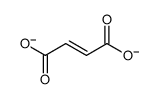 CAS#:142-42-7
CAS#:142-42-7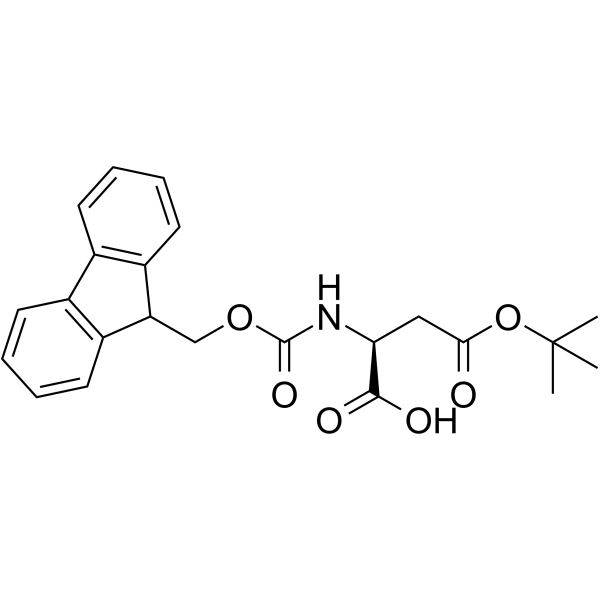 CAS#:71989-14-5
CAS#:71989-14-5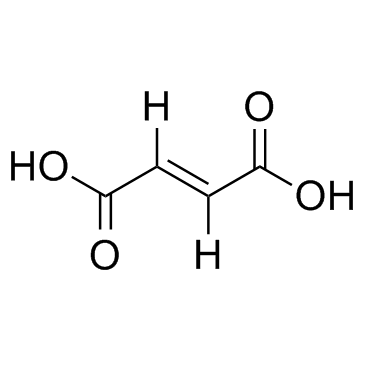 CAS#:110-17-8
CAS#:110-17-8 CAS#:2177-63-1
CAS#:2177-63-1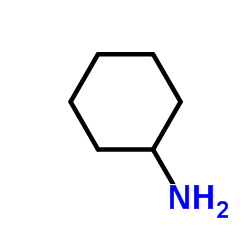 CAS#:108-91-8
CAS#:108-91-8![disodium 4-hydroxy-3-[[2-(hydroxy-oxido-phosphoryl)acetyl]amino]-4-oxo-butanoate Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/099/60342-56-5.png) CAS#:60342-56-5
CAS#:60342-56-5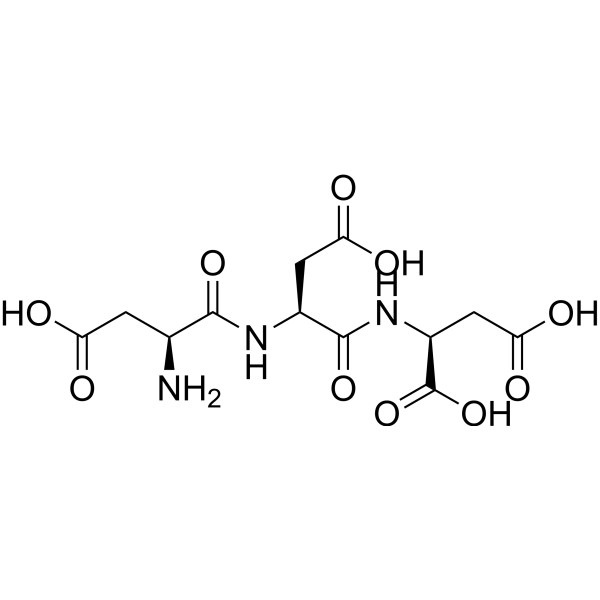 CAS#:107208-63-9
CAS#:107208-63-9 CAS#:1116-15-0
CAS#:1116-15-0 CAS#:1116-12-7
CAS#:1116-12-7 CAS#:42918-86-5
CAS#:42918-86-5 CAS#:328-42-7
CAS#:328-42-7 CAS#:56-86-0
CAS#:56-86-0 CAS#:302-72-7
CAS#:302-72-7 CAS#:4226-18-0
CAS#:4226-18-0 CAS#:32213-95-9
CAS#:32213-95-9 CAS#:16856-13-6
CAS#:16856-13-6
