N-Butylurea
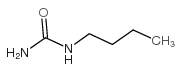
N-Butylurea structure
|
Common Name | N-Butylurea | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 592-31-4 | Molecular Weight | 116.16200 | |
| Density | 0.962 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 179.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H12N2O | Melting Point | 95-98 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 62.3ºC | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | butylurea |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 0.962 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 179.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 95-98 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C5H12N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 116.16200 |
| Flash Point | 62.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 116.09500 |
| PSA | 55.12000 |
| LogP | 1.54600 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.449 |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22;R37;R68 |
| Safety Phrases | S45-S36/37 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | YS3675000 |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
A quadruply hydrogen bonded heterocomplex displaying high-fidelity recognition.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127(51) , 18133-42, (2005) An exceptionally strong quadruply hydrogen-bonded complex is formed between 2,7-diamido-1,8-naphthyridine 3 (DAN) and the butylurea of guanosine 6 (UG) in chloroform. The UG unit can be prepared in fo... |
|
|
Comparative evaluation of fifteen anti-sickling agents.
Blood 61(4) , 693-704, (1983) Fifteen compounds reported to be inhibitors of gelation or sickling were studied by standard methods. These tests included (1) the determination of the solubility of deoxyhemoglobin S or Csat, (2) eva... |
|
|
Discovery of novel benzothiazolesulfonamides as potent inhibitors of HIV-1 protease.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 11(22) , 4769-77, (2003) The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) has been shown to be the causative agent for AIDS. The HIV virus encodes for a unique aspartyl protease that is essential for the production of enzymes and prote... |
| EINECS 209-748-4 |
| Urea,butyl |
| 1-Butylurea |
| MFCD00007956 |
| Urea,N-butyl |
| butylamine amide |
| 1-n-butylurea |
| N-BUTYLUREA |
 CAS#:111-36-4
CAS#:111-36-4 CAS#:39078-72-3
CAS#:39078-72-3 CAS#:590-28-3
CAS#:590-28-3 CAS#:109-73-9
CAS#:109-73-9 CAS#:4370-12-1
CAS#:4370-12-1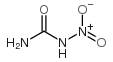 CAS#:556-89-8
CAS#:556-89-8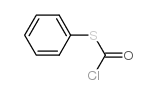 CAS#:13464-19-2
CAS#:13464-19-2 CAS#:3858-78-4
CAS#:3858-78-4 CAS#:684-93-5
CAS#:684-93-5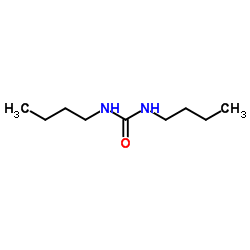 CAS#:1792-17-2
CAS#:1792-17-2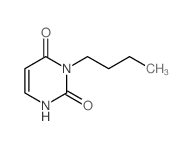 CAS#:28289-95-4
CAS#:28289-95-4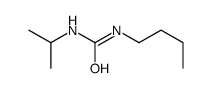 CAS#:25347-95-9
CAS#:25347-95-9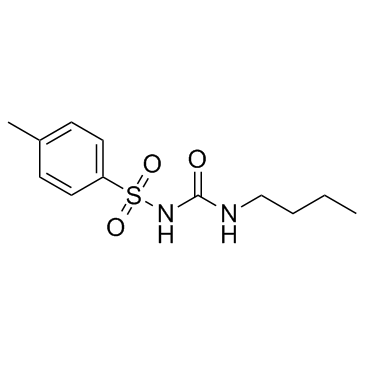 CAS#:64-77-7
CAS#:64-77-7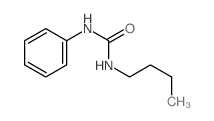 CAS#:3083-88-3
CAS#:3083-88-3![2-Propenamide,3-[[(butylamino)carbonyl]amino]-2-cyano- structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/465/6976-80-3.png) CAS#:6976-80-3
CAS#:6976-80-3 CAS#:705-06-6
CAS#:705-06-6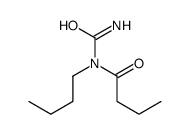 CAS#:73025-03-3
CAS#:73025-03-3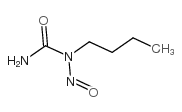 CAS#:869-01-2
CAS#:869-01-2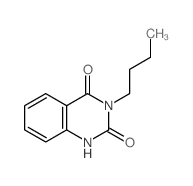 CAS#:6944-59-8
CAS#:6944-59-8
