Doxorubicinol hydrochloride
Modify Date: 2024-01-09 06:59:06
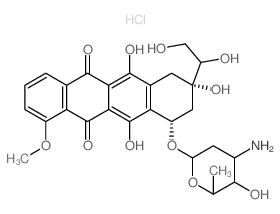
Doxorubicinol hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Doxorubicinol hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 63950-05-0 | Molecular Weight | 581.99600 | |
| Density | 1.61g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 828.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H32ClNO11 | Melting Point | 188-192ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 455ºC | |
Use of Doxorubicinol hydrochlorideDoxorubicinol hydrochloride (13-Dihydroadriamycin hydrochloride) is a secondary alcohol metabolite of Doxorubicin[1]. |
| Name | 13-Dihydroadriamycin hydrochloride |
|---|
| Description | Doxorubicinol hydrochloride (13-Dihydroadriamycin hydrochloride) is a secondary alcohol metabolite of Doxorubicin[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Doxorubicinol hydrochloride is produced by a two-electron, NADPH-dependent reduction of the Doxorubicin side-chain carbonyl group (C13) to a secondary alcohol[1]. Doxorubicinol hydrochloride has been shown to have significantly lower DNA binding activity as compared to DOX. Moreover, while Doxorubicinol hydrochloride is retained in the cytoplasm or lysosomes, Doxorubicin is mainly accumulated in the nucleus[1]. |
| In Vivo | In vivo, in tumor-bearing mice, Nilotinib, acting as ABCB1 inhibitor, is found to increase the accumulation of Doxorubicin and Doxorubicinol hydrochloride in cancer tissues. This implies that weaker anticancer activity of Doxorubicinol hydrochloride may be related to its increased affinity to ABC transporters, thus leading to a lower intracellular concentration of the agent[1]. In comparison with wild-type mice, the terminal half-life and the area under the plasma concentration-time curve of Doxorubicin in mdr1a(-/-) mice are 1.6- and 1.2-fold higher respectively. The retention of both Doxorubicin and its metabolite Doxorubicinol hydrochloride in the hearts of mdr1a(-/-) mice is substantially prolonged[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.61g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 828.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 188-192ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C27H32ClNO11 |
| Molecular Weight | 581.99600 |
| Flash Point | 455ºC |
| Exact Mass | 581.16600 |
| PSA | 209.23000 |
| LogP | 1.29540 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.716 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|