2',3'-Dideoxyinosine
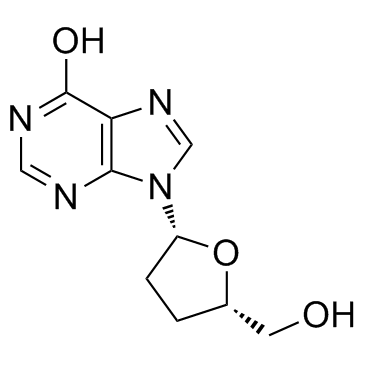
2',3'-Dideoxyinosine structure
|
Common Name | 2',3'-Dideoxyinosine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 69655-05-6 | Molecular Weight | 236.227 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 531.2±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12N4O3 | Melting Point | 193-195 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 275.0±32.9 °C | |
Use of 2',3'-DideoxyinosineDidanosine(Videx) is a reverse transcriptase inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.49 μM.Target: NRTIs; HIVDidanosine is a dideoxynucleoside compound in which the 3'-hydroxy group on the sugar moiety has been replaced by a hydrogen. This modification prevents the formation of phosphodiester linkages which are needed for the completion of nucleic acid chains. Didanosine is a potent inhibitor of HIV replication, acting as a chain-terminator of viral DNA by binding to reverse transcriptase. Didanosine demonstrated linear pharmacokinetic behavior over the dose ranges of 0.4 to 16.5 mg/kg intravenously and 0.8 to 10.2 mg/kg orally. Bioavailability of didanosine when administered as a solution with an antacid was approximately 43% for doses from 0.8 to 10.2 mg/kg in patients with AIDS and advanced AIDS-related complex. Bioavailability of didanosine from the citrate-phosphate-buffered solution, the formulation currently used in phase II and expanded access studies, was comparable to the formulation used in the phase I trials [1]. ddI might be responsible for fulminant hepatitis in all three AIDS patients. This toxic effect may be added to the list of potential adverse events occurring during ddI therapy [2]. |
| Name | didanosine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Didanosine(Videx) is a reverse transcriptase inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.49 μM.Target: NRTIs; HIVDidanosine is a dideoxynucleoside compound in which the 3'-hydroxy group on the sugar moiety has been replaced by a hydrogen. This modification prevents the formation of phosphodiester linkages which are needed for the completion of nucleic acid chains. Didanosine is a potent inhibitor of HIV replication, acting as a chain-terminator of viral DNA by binding to reverse transcriptase. Didanosine demonstrated linear pharmacokinetic behavior over the dose ranges of 0.4 to 16.5 mg/kg intravenously and 0.8 to 10.2 mg/kg orally. Bioavailability of didanosine when administered as a solution with an antacid was approximately 43% for doses from 0.8 to 10.2 mg/kg in patients with AIDS and advanced AIDS-related complex. Bioavailability of didanosine from the citrate-phosphate-buffered solution, the formulation currently used in phase II and expanded access studies, was comparable to the formulation used in the phase I trials [1]. ddI might be responsible for fulminant hepatitis in all three AIDS patients. This toxic effect may be added to the list of potential adverse events occurring during ddI therapy [2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 531.2±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 193-195 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12N4O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 236.227 |
| Flash Point | 275.0±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 236.090942 |
| PSA | 93.03000 |
| LogP | -1.31 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.798 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | 1-5 g/100 mL at 21 ºC |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | C |
| Risk Phrases | R34 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S27-S36/37/39-S45 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | NM7460700 |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 2942000000 |
|---|
|
Absence of a universal mechanism of mitochondrial toxicity by nucleoside analogs.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51 , 2531-9, (2007) Nucleoside analogs are associated with various mitochondrial toxicities, and it is becoming increasingly difficult to accommodate these differences solely in the context of DNA polymerase gamma inhibi... |
|
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI typ... |
| 9-[(2R,5S)-5-(hydroxyméthyl)tétrahydrofuran-2-yl]-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one |
| DDI |
| Videx |
| 9-[(2R,5S)-5-(Hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2-furanyl]-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one |
| 9-[(2R,5S)-5-(Hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]-9H-purin-6-ol |
| MFCD00077728 |
| Inosine, 2’,3’-dideoxy- |
| VIDEX EC |
| 2',3'-Dideoxyinosine |
| 9-[(2R,5S)-5-(Hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-one |
| 6H-Purin-6-one, 1,9-dihydro-9-[(2R,5S)-tetrahydro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-furanyl]- |
| INOSINE, 2',3'-DIDEOXY- |
| Dideoxyinosine |
| Didanosine |
| 9-[(2R,5S)-5-(Hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]-1,9-dihydro-6H-purin-6-on |
| didanosinum [INN_la] |
![N[SP]1[/SP],5'-O-dibenzyl-2',3'-dideoxyinosine Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/410/810694-79-2.png) CAS#:810694-79-2
CAS#:810694-79-2 CAS#:42867-68-5
CAS#:42867-68-5 CAS#:4097-22-7
CAS#:4097-22-7![9-[(2R,5S)-5-[[tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxymethyl]oxolan-2-yl]-3H-purin-6-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/418/177779-56-5.png) CAS#:177779-56-5
CAS#:177779-56-5 CAS#:58-63-9
CAS#:58-63-9 CAS#:389128-06-7
CAS#:389128-06-7 CAS#:119794-34-2
CAS#:119794-34-2 CAS#:119818-51-8
CAS#:119818-51-8 CAS#:5983-09-5
CAS#:5983-09-5