L-asparagine
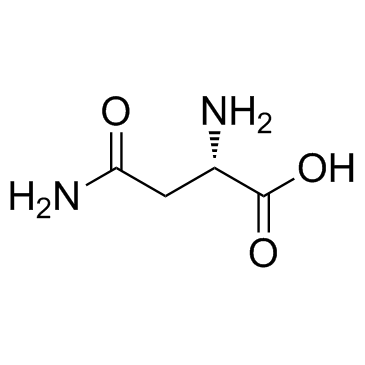
L-asparagine structure
|
Common Name | L-asparagine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 70-47-3 | Molecular Weight | 132.118 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 438.0±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H8N2O3 | Melting Point | 235 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 218.7±27.3 °C | |
Use of L-asparagineL-Asparagine is a non-essential amino acid that is involved in the metabolic control of cell functions in nerve and brain tissue. |
| Name | L-asparagine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Asparagine is a non-essential amino acid that is involved in the metabolic control of cell functions in nerve and brain tissue. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 438.0±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 235 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C4H8N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 132.118 |
| Flash Point | 218.7±27.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 132.053497 |
| PSA | 106.41000 |
| LogP | -1.51 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.533 |
| Water Solubility | 20 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Characterisation of a putative AraC transcriptional regulator from Mycobacterium smegmatis.
Tuberculosis (Edinb.) 94(6) , 664-71, (2015) MSMEG_0307 is annotated as a transcriptional regulator belonging to the AraC protein family and is located adjacent to the arylamine N-acetyltransferase (nat) gene in Mycobacterium smegmatis, in a gen... |
|
|
Development of High-purity Certified Reference Materials for 17 Proteinogenic Amino Acids by Traceable Titration Methods.
Anal. Sci. 31 , 805-14, (2015) To ensure the reliability of amino acid analyses, the National Metrology Institute of Japan of the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (NMIJ/AIST) has developed high-purit... |
|
|
Use of Commercial Dry Yeast Products Rich in Mannoproteins for White and Rosé Sparkling Wine Elaboration.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 5670-81, (2015) In sparkling wines, mannoproteins released during yeast autolysis largely affect their final quality. This process is very slow and may take several months. The aim of this work was to study the effec... |
| 4-04-00-03005 |
| ASPARAGINE,DL |
| Asn Asparagine |
| (±)-2-Aminosuccinic acid 4-amide |
| L-Asn-OH |
| Asparagine, DL- |
| H-DL-Asn-OH Monohydrate |
| L-Asparagine |
| 2-Aminosuccinamic acid |
| a-Aminosuccinamic acid |
| DL-Aspartamine |
| EINECS 200-735-9 |
| DL-ASPARAGINE |
| DL-Asn |
| DL-Asparagine monohydrate |
| DL-Asparaning H2O |
| Asn |
| L-Asn |
| H-ASN-OH |
| DL-Aspartic acid 4-amide |
| H-DL-Asn-OH |
| DL-Asparagine.H2O |
| DL-Asparagine hydrate |
| Aspartic Acid b-Amide |
| Agedoite |
| L-Aspartic monohydrate |
| Altheine |
| Asparagine |
| Asparamide |
| Crystal VI |
| MFCD00064401 |
| h-dl-asn.h |
| asparagine acid |
| (L-Asparagin)alfa-Aminosuccinamicacid |
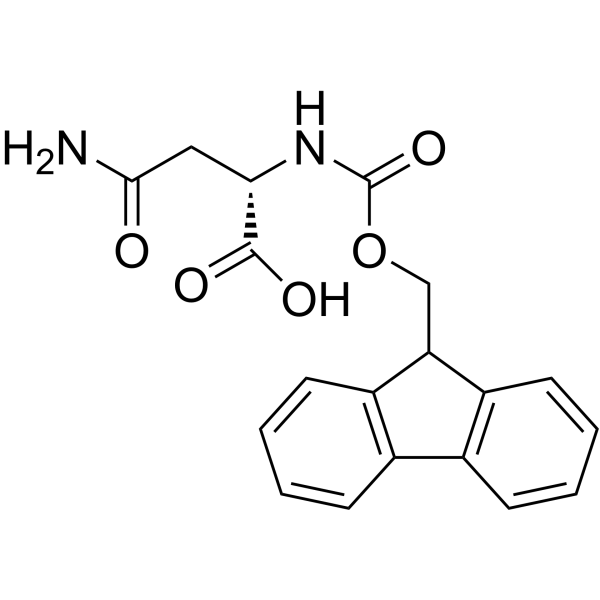 CAS#:71989-16-7
CAS#:71989-16-7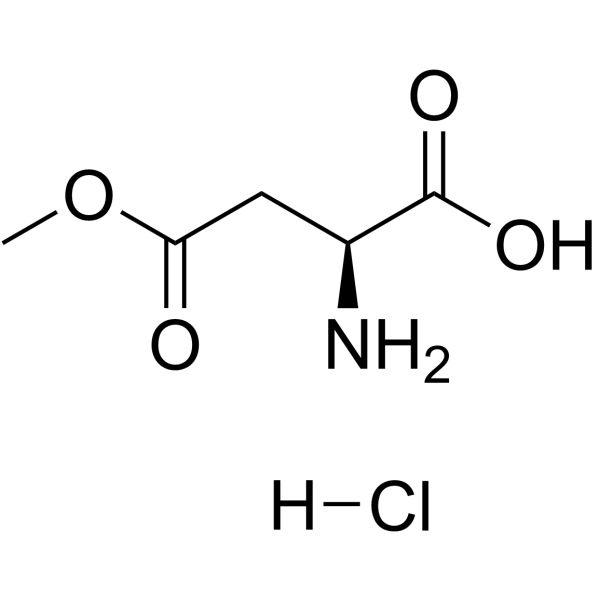 CAS#:16856-13-6
CAS#:16856-13-6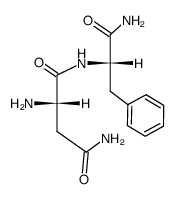 CAS#:47091-50-9
CAS#:47091-50-9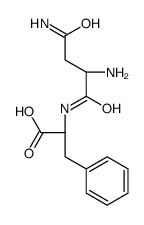 CAS#:22849-01-0
CAS#:22849-01-0 CAS#:34557-54-5
CAS#:34557-54-5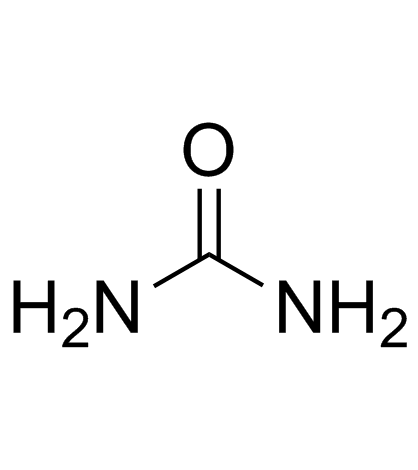 CAS#:57-13-6
CAS#:57-13-6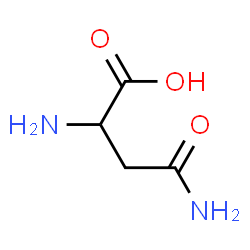 CAS#:3130-87-8
CAS#:3130-87-8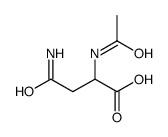 CAS#:16473-76-0
CAS#:16473-76-0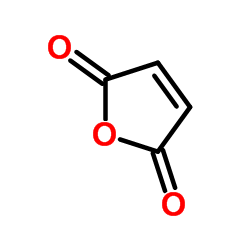 CAS#:108-31-6
CAS#:108-31-6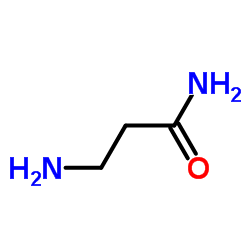 CAS#:4726-85-6
CAS#:4726-85-6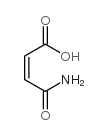 CAS#:557-24-4
CAS#:557-24-4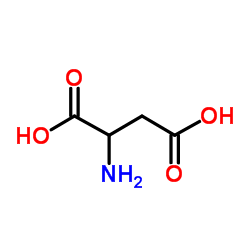 CAS#:617-45-8
CAS#:617-45-8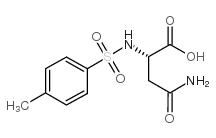 CAS#:36212-66-5
CAS#:36212-66-5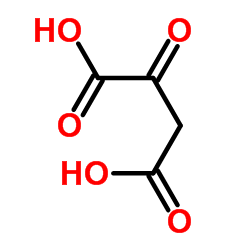 CAS#:328-42-7
CAS#:328-42-7 CAS#:33239-40-6
CAS#:33239-40-6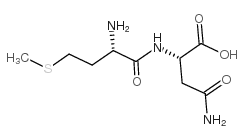 CAS#:36261-61-7
CAS#:36261-61-7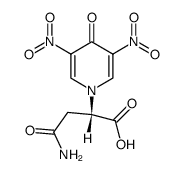 CAS#:78641-70-0
CAS#:78641-70-0 CAS#:100-01-6
CAS#:100-01-6
