Methyl viologen dichloride hydrate
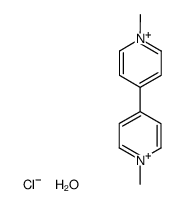
Methyl viologen dichloride hydrate structure
|
Common Name | Methyl viologen dichloride hydrate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 75365-73-0 | Molecular Weight | 239.72100 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H16ClN2O+ | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | 1,1'-dimethyl-4,4'-bipyridinediium dichloride hydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Molecular Formula | C12H16ClN2O+ |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 239.72100 |
| Exact Mass | 239.09500 |
| PSA | 16.99000 |
| LogP | 1.74030 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Symbol |



GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 + H311-H315-H319-H330-H335-H372-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P273-P280-P284-P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+,N |
| Risk Phrases | 24/25-26-36/37/38-48/25-50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-28-36/37/39-45-60-61 |
| RIDADR | UN2811 - class 6.1 - PG 1 - EHS - Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., HI: all |
| RTECS | DW2275000 |
|
Functional cloning and characterization of the multidrug efflux pumps NorM from Neisseria gonorrhoeae and YdhE from Escherichia coli.
Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52 , 3052-60, (2008) Active efflux of antimicrobial agents is one of the most important adapted strategies that bacteria use to defend against antimicrobial factors that are present in their environment. The NorM protein ... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals ... |
|
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is one of the most important reasons for drug development failure at both preapproval and postapproval stages. There has been increased interest in developing predicti... |
| methyl viologen dichloride hydrate |
| methylviologen dichloride hydrate |
| Paraquatdichloridehydrate |