Trifluorostibine
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 11:47:41

Trifluorostibine structure
|
Common Name | Trifluorostibine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7783-56-4 | Molecular Weight | 178.755 | |
| Density | 4.379 | Boiling Point | 376ºC | |
| Molecular Formula | F3Sb | Melting Point | 292ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 376ºC | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | Antimony trifluoride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 4.379 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 376ºC |
| Melting Point | 292ºC |
| Molecular Formula | F3Sb |
| Molecular Weight | 178.755 |
| Flash Point | 376ºC |
| Exact Mass | 177.899033 |
| LogP | 1.26060 |
Synonym:Antimonous Trifluoride; Trifluoroantimony Section 2 - COMPOSITION, INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS
Risk Phrases: 23/24/25 51/53 Section 3 - HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION EMERGENCY OVERVIEW
Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment.Corrosive.Water-reactive. Potential Health Effects Eye: When substance becomes wet or comes in contact with moisture of the mucous membranes, it will cause irritation. May cause chemical conjunctivitis and corneal damage. Skin: Contact with skin causes irritation and possible burns, especially if the skin is wet or moist. May cause skin rash (in milder cases), and cold and clammy skin with cyanosis or pale color. Ingestion: May cause severe and permanent damage to the digestive tract. May cause liver damage. May cause perforation of the digestive tract. Inorganic fluorides can be harmful. Acute exposure to fluorine compounds can lead to digestive tract burns, and abdominal pain. Contains fluoride. Fluoride can reduce calcium levels leading to fatal hypocalcemia. May cause systemic effects. Inhalation: Causes chemical burns to the respiratory tract. Inhalation may be fatal as a result of spasm, inflammation, edema of the larynx and bronchi, chemical pneumonitis and pulmonary edema. Aspiration may lead to pulmonary edema. May cause systemic effects. Chronic: Chronic inhalation and ingestion may cause chronic fluoride poisoning (fluorosis) characterized by weight loss, weakness, anemia, brittle bones, and stiff joints. Chronic inhalation may cause nasal septum ulceration and perforation. Effects may be delayed. Chronic exposure to fluoride compounds may cause systemic toxicity. Section 4 - FIRST AID MEASURES Eyes: Get medical aid immediately. Do NOT allow victim to rub eyes or keep eyes closed. Extensive irrigation with water is required (at least 30 minutes). Skin: Get medical aid immediately. Immediately flush skin with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes while removing contaminated clothing and shoes. Wash clothing before reuse. Destroy contaminated shoes. If water-reactive products are embedded in the skin, no water should be applied. The embedded products should be covered with a light oil. Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting. If victim is conscious and alert, give 2-4 cupfuls of milk or water. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Get medical aid immediately. Inhalation: Get medical aid immediately. Remove from exposure and move to fresh air immediately. If not breathing, give artificial respiration. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. Do NOT use mouth-to-mouth resuscitation. If breathing has ceased apply artificial respiration using oxygen and a suitable mechanical device such as a bag and a mask. Notes to Physician: Section 5 - FIRE FIGHTING MEASURES General Information: As in any fire, wear a self-contained breathing apparatus in pressure-demand, MSHA/NIOSH (approved or equivalent), and full protective gear. During a fire, irritating and highly toxic gases may be generated by thermal decomposition or combustion. Not flammable, but reacts with most metals to form flammable hydrogen gas. Water Reactive. Material will react with water and may release a flammable and/or toxic gas. Use water spray to keep fire-exposed containers cool. Containers may explode when heated or if contaminated with water. When heated to decomposition, antimony trifluoride emits very toxic fumes of hydrogen fluoride and antimony. Extinguishing Media: If water is the only media available, use in flooding amounts. Do NOT get water inside containers. For large fires, use water spray, fog or alcohol-resistant foam. Do NOT use straight streams of water. Most foams will react with the material and release corrosive/toxic gases. Contact professional fire-fighters immediately. Cool containers with flooding quantities of water until well after fire is out. For small fires, use carbon dioxide (except for cyanides), dry chemical, dry sand, and alcohol-resistant foam. Section 6 - ACCIDENTAL RELEASE MEASURES General Information: Use proper personal protective equipment as indicated in Section 8. Spills/Leaks: Vacuum or sweep up material and place into a suitable disposal container. Avoid runoff into storm sewers and ditches which lead to waterways. Clean up spills immediately, observing precautions in the Protective Equipment section. Avoid generating dusty conditions. Provide ventilation. Do not expose spill to water. Section 7 - HANDLING and STORAGE Handling: Wash thoroughly after handling. Wash hands before eating. Remove contaminated clothing and wash before reuse. Use only in a well-ventilated area. Do not allow water to get into the container because of violent reaction. Do not breathe dust, vapor, mist, or gas. Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. Keep container tightly closed. Do not allow contact with water. Use only in a chemical fume hood. Discard contaminated shoes. Keep from contact with moist air and steam. Storage: Store in a cool, dry place. Keep container closed when not in use. Store in a tightly closed container. Keep away from water. Corrosives area. Section 8 - EXPOSURE CONTROLS, PERSONAL PROTECTION Engineering Controls: Use explosion-proof ventilation equipment. Facilities storing or utilizing this material should be equipped with an eyewash facility and a safety shower. Use adequate ventilation to keep airborne concentrations low. Exposure Limits CAS# 7783-56-4: United Kingdom, WEL - TWA: (listed as antimony compounds): 0.5 mg TWA (except stibine, as Sb) United Kingdom, WEL - STEL: (listed as antimony compounds): 1.5 m STEL (except stibine, as Sb) United States OSHA: 0.5 mg/m3 TWA (listed under Antimony).2.5 mg TWA (as F) (listed under Fluorides).2.5 mg/m3 TWA (as F) (liste under Fluorides).0.5 mg/m3 TWA (as Sb) (listed under Antimony compounds). Belgium - TWA: (listed as antimony compounds): 0.5 mg/m3 VLE (as France - VME: (listed as antimony compounds): 0.5 mg/m3 VME (as S Germany: (listed as antimony compounds): 0.5 mg/m3 VME (as Sb) Japan: (listed as antimony compounds): 0.1 mg/m3 OEL (except stib as Sb) Malaysia: (listed as antimony compounds): 0.5 mg/m3 TWA (as Sb) Netherlands: (listed as fluorides): 3.5 mg/m3 STEL (as F) Netherlands: (listed as antimony compounds): 0.5 mg/m3 MAC (as Sb Russia: 0.3 mg/m3 TWA Russia: (listed as antimony): 0.2 mg/m3 STEL Spain: (listed as antimony compounds): 0.5 mg/m3 VLA-ED (except antimony hydride, as Sb) Personal Protective Equipment Eyes: Wear appropriate protective eyeglasses or chemical safety goggles as described by OSHA's eye and face protection regulations in 29 CFR 1910.133 or European Standard EN166. Skin: Wear appropriate protective gloves to prevent skin exposure. Clothing: Wear appropriate protective clothing to prevent skin exposure. Respirators: A respiratory protection program that meets OSHA's 29 CFR 1910.134 and ANSI Z88.2 requirements or European Standard EN 149 must be followed whenever workplace conditions warrant respirator use. Section 9 - PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES Physical State: Solid Color: white Odor: Odorless. pH: Not available. Vapor Pressure: 26kpa @ .26atm Viscosity: Not available. Boiling Point: 376 deg C Freezing/Melting Point: 292 deg C Autoignition Temperature: Not applicable. Flash Point: Not applicable. Explosion Limits, lower: Not available. Explosion Limits, upper: Not available. Decomposition Temperature: Not available. Solubility in water: Soluble in water. Specific Gravity/Density: 4.38 Molecular Formula: F3Sb Molecular Weight: 178.7052 Section 10 - STABILITY AND REACTIVITY Chemical Stability: Stable under normal temperatures and pressures. Combines vigorously or explosively with water. Reaction with water generates much heat, which will increase the concentration of fumes, hydrogen fluoride and antimony, in the air. Conditions to Avoid: Incompatible materials, dust generation, exposure to moist air or water. Incompatibilities with Other Materials: Strong oxidizing agents, perchloric acid, water. Hazardous Decomposition Products: Irritating and toxic fumes and gases, hydrogen fluoride gas, antimony/antimony oxides. Hazardous Polymerization: Has not been reported Section 11 - TOXICOLOGICAL INFORMATION RTECS#: CAS# 7783-56-4: CC5150000 LD50/LC50: CAS# 7783-56-4: Oral, mouse: LD50 = 804 mg/kg. Carcinogenicity: Antimony Trifluoride - Not listed by ACGIH, IARC, or NTP. Other: See actual entry in RTECS for complete information. Section 12 - ECOLOGICAL INFORMATION Section 13 - DISPOSAL CONSIDERATIONS Dispose of in a manner consistent with federal, state, and local regulations. Section 14 - TRANSPORT INFORMATION IATA Shipping Name: Not regulated. Hazard Class: (6.1) UN Number: Packing Group: IMO Shipping Name: Not regulated. Hazard Class: (6.1) UN Number: Packing Group: RID/ADR Shipping Name: Not regulated. Hazard Class: 8 UN Number: Packing group: II USA RQ: CAS# 7783-56-4: 1000 lb final RQ; 454 kg final RQ Section 15 - REGULATORY INFORMATION European/International Regulations European Labeling in Accordance with EC Directives Hazard Symbols: T N Risk Phrases: R 23/24/25 Toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed. R 51/53 Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. Safety Phrases: S 7 Keep container tightly closed. S 26 In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice. S 45 In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label where possible). S 61 Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions/safety data sheets. WGK (Water Danger/Protection) CAS# 7783-56-4: No information available. Canada CAS# 7783-56-4 is listed on Canada's DSL List. CAS# 7783-56-4 is not listed on Canada's Ingredient Disclosure List. US FEDERAL TSCA CAS# 7783-56-4 is listed on the TSCA inventory. SECTION 16 - ADDITIONAL INFORMATION N/A |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS06, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 + H311 + H331-H314-H411 |
| Precautionary Statements | Missing Phrase - N15.00950417-P260-P280-P303 + P361 + P353-P304 + P340 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R23/24/25;R51/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S45-S61-S7 |
| RIDADR | UN 1733/1549 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CC5150000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| Trifluorostibine |
| antimony fluoride |
| MFCD00011218 |
| Stibine, trifluoro- |
| antimony(III) trifluoride |
| EINECS 232-009-2 |
| antimony(III) fluoride |
| tribromostibine |
| antimony(V) fluoride |
| Antimony(3+) trifluoride |
 CAS#:10025-91-9
CAS#:10025-91-9 CAS#:7440-36-0
CAS#:7440-36-0 CAS#:7783-70-2
CAS#:7783-70-2 CAS#:432-05-3
CAS#:432-05-3 CAS#:7789-33-5
CAS#:7789-33-5 CAS#:7664-39-3
CAS#:7664-39-3 CAS#:7783-54-2
CAS#:7783-54-2 CAS#:7791-16-4
CAS#:7791-16-4 CAS#:7783-81-5
CAS#:7783-81-5![N-[bis(trifluoromethyl)amino]oxy-1,1,1-trifluoro-N-(trifluoromethyl)methanamine Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/305/6141-72-6.png) CAS#:6141-72-6
CAS#:6141-72-6 CAS#:105396-09-6
CAS#:105396-09-6 CAS#:373-74-0
CAS#:373-74-0 CAS#:420-58-6
CAS#:420-58-6 CAS#:430-88-6
CAS#:430-88-6 CAS#:471-43-2
CAS#:471-43-2 CAS#:359-28-4
CAS#:359-28-4 CAS#:430-89-7
CAS#:430-89-7 CAS#:358-60-1
CAS#:358-60-1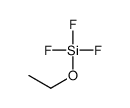 CAS#:460-55-9
CAS#:460-55-9
