1-Nitronaphthalene
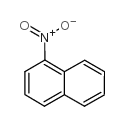
1-Nitronaphthalene structure
|
Common Name | 1-Nitronaphthalene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 86-57-7 | Molecular Weight | 173.16800 | |
| Density | 1.223 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | 304 °C(lit.) | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H7NO2 | Melting Point | 56 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 164 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | 1-nitronaphthalene |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.223 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 304 °C(lit.) |
| Melting Point | 56 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C10H7NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 173.16800 |
| Flash Point | 164 °C |
| Exact Mass | 173.04800 |
| PSA | 45.82000 |
| LogP | 3.27120 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, strong reducing agents. Mixtures with sulfuric or nitric acid are dangerous. |
| Water Solubility | 0.022 g/L |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS02, GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H228-H301 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P301 + P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R25;R40 |
| Safety Phrases | S16-S45-S60-S61-S28A |
| RIDADR | UN 2538 4.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | QJ9720000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 4.1 |
| HS Code | 29042000 |
| HS Code | 2904209090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2904209090 derivatives containing only nitro or only nitroso groups。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:5.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Combination of precolumn nitro-reduction and ultraperformance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection for the sensitive quantification of 1-nitronaphthalene, 2-nitrofluorene, and 1-nitropyrene in meat products.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63(12) , 3161-7, (2015) Carcinogenic nitropolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (nitro-PAHs) are ubiquitous in the ambient environment. They are emitted predominantly from internal combustion engines and by reacting polycyclic ar... |
|
|
Determination of trace level genotoxic impurities in small molecule drug substances using conventional headspace gas chromatography with contemporary ionic liquid diluents and electron capture detection.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1361 , 217-28, (2014) Ionic liquids (ILs) were used as a new class of diluents for the analysis of two classes of genotoxic impurities (GTIs), namely, alkyl/aryl halides and nitro-aromatics, in small molecule drug substanc... |
|
|
Nitropolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are inducers of mitotic homologous recombination in the wing-spot test of Drosophila melanogaster.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 46(7) , 2344-8, (2008) In this study, the widespread environmental pollutants 1-nitronaphthalene (1NN), 1,5-dinitronaphthalene (1,5DNN), 2-nitrofluorene (2NF) and 9-nitroanthracene (9NA), were investigated for genotoxicity ... |
| MFCD00003913 |
| 1-Nitronaphthalin |
| EINECS 201-684-5 |
| 1-Nitronaphthalene |
| nitro-naphthalene |
| I-P#itronaphthalin |
| 1-Nitronphthalene |
| 1-nitro-naphthalene |
| 1-Nitronaftalen |
| 1-nitronaphtalene |
| 1-nitro-naphthalen |