2,6-xylidine

2,6-xylidine structure
|
Common Name | 2,6-xylidine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 87-62-7 | Molecular Weight | 121.180 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 217.9±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H11N | Melting Point | 10-12 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 91.1±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | 2,6-dimethylaniline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 217.9±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 10-12 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H11N |
| Molecular Weight | 121.180 |
| Flash Point | 91.1±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 121.089149 |
| PSA | 26.02000 |
| LogP | 1.86 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.1±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.559 |
| Water Solubility | 7.5 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312 + H332-H315-H335-H351-H411 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P273-P280 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22;R37/38;R40;R51/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S23-S25-S36/37-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 1711 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | ZE9275000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 29214910 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2921430090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2921430090 toluidines and their derivatives; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Simultaneous Determination of Xylazine and 2,6-Xylidine in Blood and Urine by Auto Solid-Phase Extraction and Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Quadrupole-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry.
J. Anal. Toxicol. 39 , 444-50, (2015) Xylazine as veterinary medicine for sedation, but intoxication cases in humans were identified in the last few years. A highly sensitive method is required for analyzing xylazine and its metabolites i... |
|
|
A Novel Method for Assessing Drug Degradation Product Safety Using Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Models and Stochastic Risk Assessment.
J. Pharm. Sci. 104 , 3101-19, (2015) Patient safety risk due to toxic degradation products is a potentially critical quality issue for a small group of useful drug substances. Although the pharmacokinetics of toxic drug degradation produ... |
|
|
Concentrations of dimethylaniline and other metabolites in milk and tissues of dairy cows treated with lidocaine.
Food Addit. Contam. Part A. Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 32 , 1256-64, (2015) Lidocaine is a topical anaesthetic drug used in dairy cows for laparotomy (caesarean section, abomasal displacement). Because there are no registered drugs for this indication, it can be applied under... |
| o-Xylidine |
| 2-Amino-1,3-xylene |
| 2,6-dimethyl-aniline |
| Benzene, 2-amino-1,3-dimethyl- |
| 1-amino-2,6-dimethybenzene |
| Benzenamine,2,6-dimethyl |
| 2,6-xylidine |
| 2,6-dimethylphenylamine |
| 2,6-dimethylbenzeneamine |
| aniline, 2,6-dimethyl- |
| MFCD00007747 |
| 2-amino-1,3-dimethylbenzene |
| Benzenamine, 2,6-dimethyl- |
| 2,6-Dimethylbenzenamine |
| 2,6-Dimethylaniline |
| 2-Amino-m-xylene |
| 2,5-DIMETHOXYTOLUENE |
| 1-amino-2,6-dimethylbenzene |
| 2,6-methylaniline |
| EINECS 201-758-7 |
| 2,6-dimethyl aniline |
| Bupivacaine Impurity 8 |
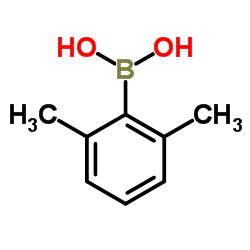 CAS#:100379-00-8
CAS#:100379-00-8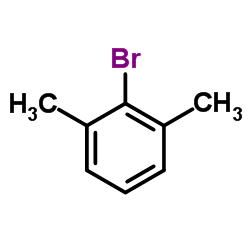 CAS#:576-22-7
CAS#:576-22-7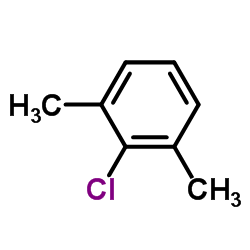 CAS#:6781-98-2
CAS#:6781-98-2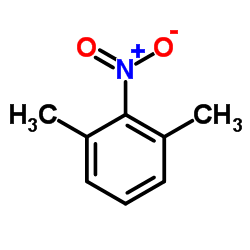 CAS#:81-20-9
CAS#:81-20-9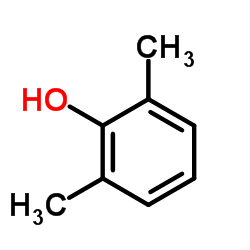 CAS#:576-26-1
CAS#:576-26-1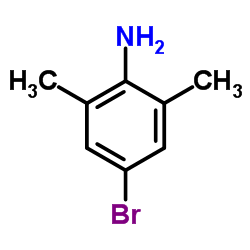 CAS#:24596-19-8
CAS#:24596-19-8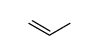 CAS#:187737-37-7
CAS#:187737-37-7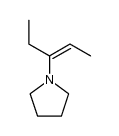 CAS#:286851-15-8
CAS#:286851-15-8 CAS#:107-02-8
CAS#:107-02-8 CAS#:10553-07-8
CAS#:10553-07-8 CAS#:106699-92-7
CAS#:106699-92-7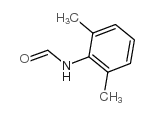 CAS#:607-92-1
CAS#:607-92-1 CAS#:527-61-7
CAS#:527-61-7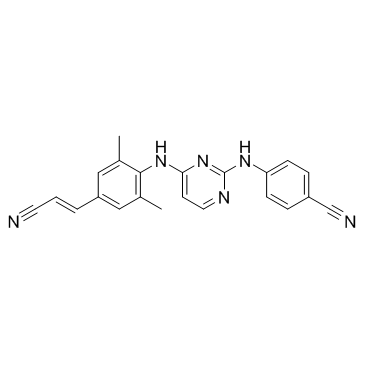 CAS#:500287-72-9
CAS#:500287-72-9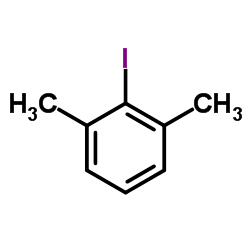 CAS#:608-28-6
CAS#:608-28-6 CAS#:4397-14-2
CAS#:4397-14-2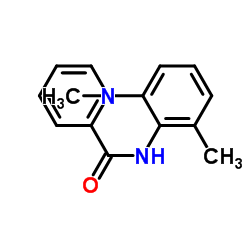 CAS#:39627-98-0
CAS#:39627-98-0 CAS#:3176-66-7
CAS#:3176-66-7
