2-Chloro-ε-caprolactone
Modify Date: 2024-04-05 09:53:16
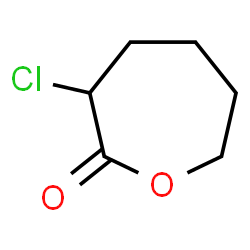
2-Chloro-ε-caprolactone structure
|
Common Name | 2-Chloro-ε-caprolactone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 89727-99-1 | Molecular Weight | 148.59 | |
| Density | 1.19±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) | Boiling Point | 108-111 °C(Press: 3 Torr) | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H9ClO2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 145.6±20.8 °C | |
Use of 2-Chloro-ε-caprolactoneDescription 2-Chloro-ε-caprolactone (ClCL) is a biomaterial that can be prepared by the Baeyer-Villiger oxidation of α-chlorocyclohexanone. It can be copolymerized with ε-caprolactone for the formation of Poly(2-chloro-ε-caprolactone).2-Chloro-ε-caprolactone (or α-Chloro-ε-caprolactone) is a functionalized biodegradable monomer. This monomer can be polymerized using ring-opening polymerization to yield a chloride-functionalized polymer backbone that can either be further functionalized with small molecules or used in the synthesis of graft co-polymers. |
| Name | 2-Chloro-ε-caprolactone |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.19±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 108-111 °C(Press: 3 Torr) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H9ClO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 148.59 |
| Flash Point | 145.6±20.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 148.029114 |
| LogP | 0.31 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.464 |
| α-Chloro-ε-caprolactone, 2-Chloro-1-oxacycloheptan-2-one, αClεCL |
| MFCD20622420 |