α-cyano-2,4-difluorocinnamic acid
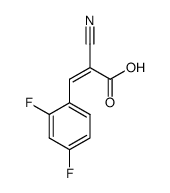
α-cyano-2,4-difluorocinnamic acid structure
|
Common Name | α-cyano-2,4-difluorocinnamic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 953905-51-6 | Molecular Weight | 209.14900 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H5F2NO2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | α-cyano-2,4-difluorocinnamic acid |
|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H5F2NO2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 209.14900 |
| Exact Mass | 209.02900 |
| PSA | 61.09000 |
| LogP | 1.95638 |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312 + H332-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
4-Chloro-alpha-cyanocinnamic acid is an advanced, rationally designed MALDI matrix.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105(34) , 12200-5, (2008) Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) has become an enabling technology for the fields of protein mass spectrometry (MS) and proteomics. Despite its widespread use, for example, in prote... |
|
|
Ion yields in UV-MALDI mass spectrometry as a function of excitation laser wavelength and optical and physico-chemical properties of classical and halogen-substituted MALDI matrixes.
Anal. Chem. 84(15) , 6567-76, (2012) The laser wavelength constitutes a key parameter in ultraviolet-matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-mass spectrometry (UV-MALDI-MS). Optimal analytical results are only achieved at laser wavel... |
|
|
The new matrix 4-chloro-alpha-cyanocinnamic acid allows the detection of phosphatidylethanolamine chloramines by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.
J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 20(5) , 867-74, (2009) Phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) are abundant lipid constituents of the cellular membrane. The amino group of PEs exhibits high reactivity with hypochlorous acid that is generated under inflammatory co... |