2,4-Di-t-butylphenol
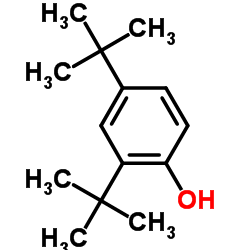
2,4-Di-t-butylphenol structure
|
Common Name | 2,4-Di-t-butylphenol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 96-76-4 | Molecular Weight | 206.324 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 265.5±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H22O | Melting Point | 53-56 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 115.0±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 2,4-Di-t-butylphenol2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol is an endogenous metabolite. |
| Name | 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol is an endogenous metabolite. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 265.5±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 53-56 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C14H22O |
| Molecular Weight | 206.324 |
| Flash Point | 115.0±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 206.167068 |
| PSA | 20.23000 |
| LogP | 4.86 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.499 |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with acid chlorides, oxidizing agents, acid anhydrides, copper, copper alloys, bases, brass. |
| Water Solubility | practically insoluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P305 + P351 + P338-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/38;R43;R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37-S61-S37/39-S29-S24-S45-S36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | UN 2430 8/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | SK8260000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 9 |
| HS Code | 29071900 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
| HS Code | 2907199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2907199090 other monophenols VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:5.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Development and application of a non-targeted extraction method for the analysis of migrating compounds from plastic baby bottles by GC-MS.
Food Addit. Contam. Part A. Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 31(12) , 2090-102, (2014) In 2011, the European Union prohibited the production of polycarbonate (PC) baby bottles due to the toxic effects of the PC monomer bisphenol-A. Therefore, baby bottles made of alternative materials, ... |
|
|
Cellular apoptosis and cytotoxicity of phenolic compounds: a quantitative structure-activity relationship study.
J. Med. Chem. 48 , 7234-42, (2005) In this comprehensive study on the caspase-mediated apoptosis-inducing effect of 51 substituted phenols in a murine leukemia cell line (L1210), we determined the concentrations needed to induce caspas... |
|
|
Human exposure assessment to a large set of polymer additives through the analysis of urine by solid phase extraction followed by ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1423 , 111-23, (2015) Polymer items are extensively present in the human environment. Humans may be consequently exposed to some compounds, such as additives, incorporated in these items. The objective of this work is to a... |
| 2,4-ditert-butylphenol |
| 2,4-Di-tert-butyl-phenol |
| phenol, 2,4-di-t-butyl- |
| 2,4-Bis(2-methyl-2-propanyl)phenol |
| 4,6-di-tert-butylphenol |
| Phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)- |
| 1-Hydroxy-2,4-di-tert-butylbenzene |
| 2,4-Di-t-butylphenol |
| MFCD00008828 |
| EINECS 202-532-0 |
| 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol |
| 2,4-Bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenol |
 CAS#:32857-07-1
CAS#:32857-07-1 CAS#:128-39-2
CAS#:128-39-2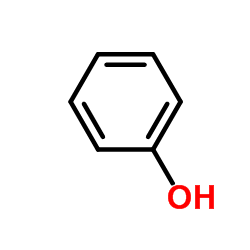 CAS#:108-95-2
CAS#:108-95-2 CAS#:115-11-7
CAS#:115-11-7 CAS#:507-19-7
CAS#:507-19-7 CAS#:513-35-9
CAS#:513-35-9 CAS#:1014-60-4
CAS#:1014-60-4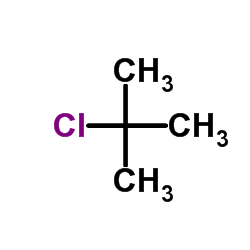 CAS#:507-20-0
CAS#:507-20-0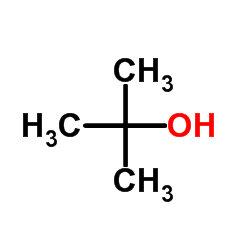 CAS#:75-65-0
CAS#:75-65-0![5,7-ditert-butyl-1-oxaspiro[2.5]octa-5,7-dien-4-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/220/39117-89-0.png) CAS#:39117-89-0
CAS#:39117-89-0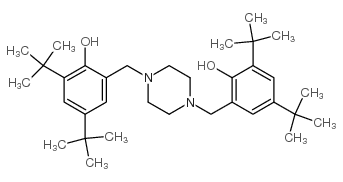 CAS#:110546-20-8
CAS#:110546-20-8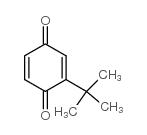 CAS#:3602-55-9
CAS#:3602-55-9 CAS#:2460-77-7
CAS#:2460-77-7![2-(2H-Benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-2-yl)-4,6-di-tert-butylphenol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/150/3846-71-7.png) CAS#:3846-71-7
CAS#:3846-71-7 CAS#:3864-99-1
CAS#:3864-99-1 CAS#:37942-07-7
CAS#:37942-07-7 CAS#:120695-70-7
CAS#:120695-70-7![6,8-di-tert-butyl-3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-2-hydroxybenzyl)-2H-3,4-dihydrobenz[e]-1,3-oxazine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/392/120695-69-4.png) CAS#:120695-69-4
CAS#:120695-69-4
