DL-Glutamic acid-d3
Modify Date: 2024-01-18 19:30:47
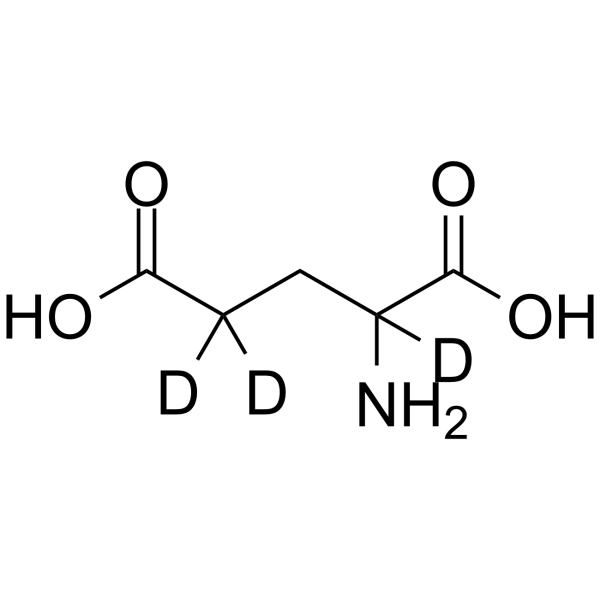
DL-Glutamic acid-d3 structure
|
Common Name | DL-Glutamic acid-d3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 96927-56-9 | Molecular Weight | 150.148 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 333.8±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H6D3NO4 | Melting Point | 185 °C (dec)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 155.7±25.1 °C | |
Use of DL-Glutamic acid-d3DL-Glutamic acid-d3 is the deuterium labeled DL-Glutamic acid. DL-Glutamic acid is the conjugate acid of Glutamic acid, which acts as a fundamental metabolite. Comparing with the second phase of polymorphs α and β L-Glutamic acid, DL-Glutamic acid presents better stability[1]. |
| Name | dl-glutamic-2,4,4-d3 acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | DL-Glutamic acid-d3 is the deuterium labeled DL-Glutamic acid. DL-Glutamic acid is the conjugate acid of Glutamic acid, which acts as a fundamental metabolite. Comparing with the second phase of polymorphs α and β L-Glutamic acid, DL-Glutamic acid presents better stability[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 333.8±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 185 °C (dec)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C5H6D3NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 150.148 |
| Flash Point | 155.7±25.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 150.071991 |
| PSA | 100.62000 |
| LogP | -1.43 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.522 |
| Storage condition | -20C |
| (2,4,4-H)Glutamic acid |
| Glutamic-2,4,4-d acid |