Biotin sodium
Modify Date: 2024-01-14 18:52:46
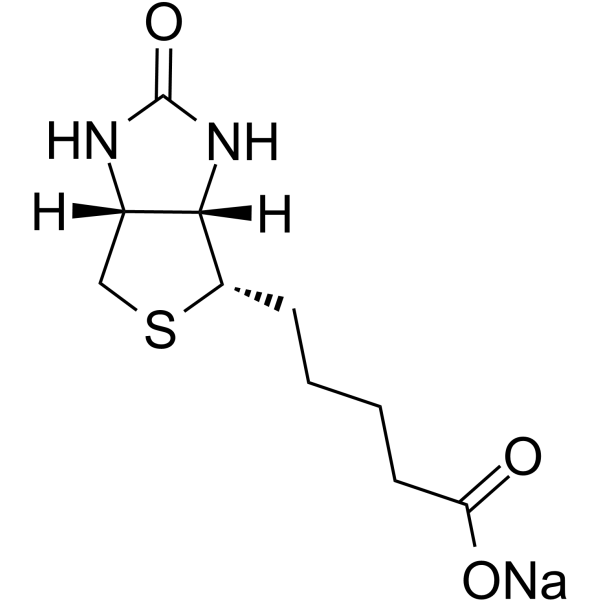
Biotin sodium structure
|
Common Name | Biotin sodium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 56085-82-6 | Molecular Weight | 266.29 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H15N2NaO3S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Biotin sodiumBiotin (Vitamin B7) sodium is a water-soluble B vitamin and serves as a coenzyme for five carboxylases in humans, involved in the synthesis of fatty acids, isoleucine, and valine, and in gluconeogenesis. Biotin sodium is necessary for cell growth, the production of fatty acids, and the metabolism of fats and amino acids[1][2][3]. |
| Name | Biotin sodium |
|---|
| Description | Biotin (Vitamin B7) sodium is a water-soluble B vitamin and serves as a coenzyme for five carboxylases in humans, involved in the synthesis of fatty acids, isoleucine, and valine, and in gluconeogenesis. Biotin sodium is necessary for cell growth, the production of fatty acids, and the metabolism of fats and amino acids[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Microbial Metabolite Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
[1]. Zempleni, et al. Biotin biochemistry and human requirements. J Nutr Biochem, 1999. 10(3): p. 128-38. [3]. Zempleni J, et al. Biotin. Biofactors. 2009 Jan-Feb;35(1):36-46. |
| Molecular Formula | C10H15N2NaO3S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 266.29 |