Fmoc-Aeg(N3)-OH
Modify Date: 2024-09-15 23:31:50
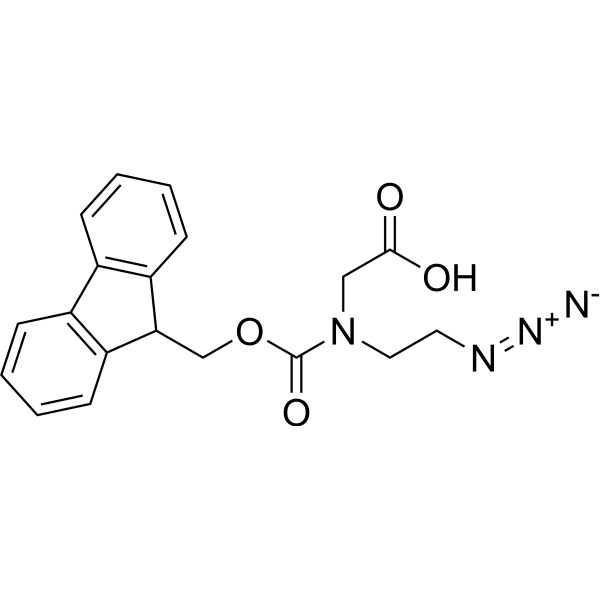
Fmoc-Aeg(N3)-OH structure
|
Common Name | Fmoc-Aeg(N3)-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1935981-35-3 | Molecular Weight | 366.37 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H18N4O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Fmoc-Aeg(N3)-OHFmoc-Aeg(N3)-OH is a click chemistry reagent containing an Azide. Alkylating the Nitrogen of an amide bond results in peptoid structures, which leads to conformational restrains, like N-methylation and allows backbone derivatisation. Altering cytotoxicity, bacterial cell selectivity and receptor pharmacology through formation of peptoid derivatives have been published for Cilengitide, Piscidin 1, and MC3, MC4 and MC5 receptor agonist. This building block enables design of macrocycles through intermolecular crosslinking or backbone stabilization through intermolecular ring-closure. This compound is a potential building block for the construction of (customized) peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) and for peptoid synthesis[1]. |
| Name | Fmoc-Aeg(N3)-OH |
|---|
| Description | Fmoc-Aeg(N3)-OH is a click chemistry reagent containing an Azide. Alkylating the Nitrogen of an amide bond results in peptoid structures, which leads to conformational restrains, like N-methylation and allows backbone derivatisation. Altering cytotoxicity, bacterial cell selectivity and receptor pharmacology through formation of peptoid derivatives have been published for Cilengitide, Piscidin 1, and MC3, MC4 and MC5 receptor agonist. This building block enables design of macrocycles through intermolecular crosslinking or backbone stabilization through intermolecular ring-closure. This compound is a potential building block for the construction of (customized) peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) and for peptoid synthesis[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Molecular Formula | C19H18N4O4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 366.37 |