303-97-9
| Name | ubiquinone-9 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
ubiquinone-9
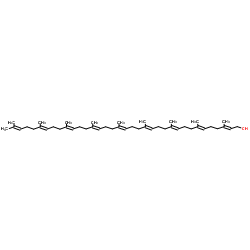
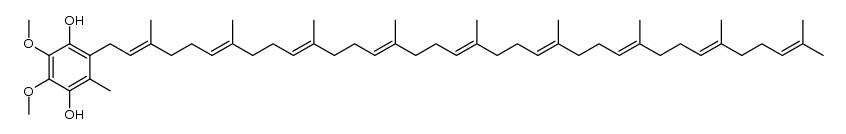
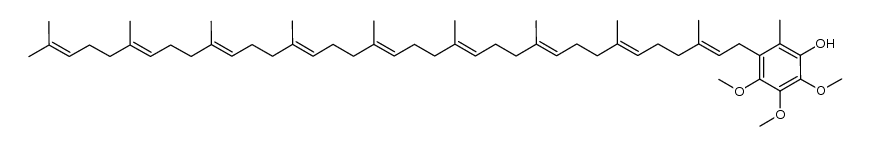
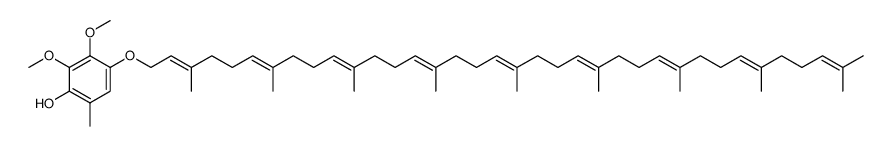
Ubidecarenone impurity D Coenzyme Q9 Coenzyme Q9 Ubiquinone Q(sub 9) CoQ(sub 9) Coenzyme Q(sub 9) 2,3-dimethoxy-6-methyl-5-nonaisoprenoid-1,4-benzoquinone 2,3-Dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-[(2E,6E,10E,14E,18E,22E,26E,30E)-3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35-nonamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34-hexatriacontanonaen-1-yl]-1,4-benzoquinone All-Trans Coenzyme Q9 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-2-<(all-E)-3',7',11',15',19',23',27',31',35'-nonamethylhexatriaconta-2',6',10',14',18',22',26',30',34',nonaenyl>cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1,4-dion CoQ9 ubiquinone Q9 2,5-Cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione, 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-[(2E,6E,10E,14E,18E,22E,26E,30E)-3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35-nonamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34-hexatriacontanonaen-1-yl]- 2,3-dimethoxy-5-methyl-6-[(2E,6E,10E,14E,18E,22E,26E,30E)-3,7,11,15,19,23,27,31,35-nonamethylhexatriaconta-2,6,10,14,18,22,26,30,34-nonaenyl]cyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione Ubidecarenone Related Compound A Ubiquinone-45 Q-9 Ubiquinone-45 Ubiquinone-9 |
| Description | Coenzyme Q9, a nine isoprenyl group-containing member of the ubiquinone family, is a normal constituent of human plasma. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Both CoQ9 and CoQ10 are equally cardioprotective, as evidenced by their abilities to improve left ventricular performance and to reduce myocardial infarct size and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. HPLC analysis reveals that a substantial portion of CoQ9 has been converted into CoQ10[1]. CoQ10 and CoQ9 are components of themitochondrial respiratory chain in mammals and can regulate some mitochondrial proteins/functions. Soybean, corn, and rapeseed oils are very rich sources of CoQ10, whereas CoQ9 has been found in high concentrations in corn oil[2]. |
| In Vivo | The lack of a functional CoQ9 protein in homozygous CoQ9 mutant (CoQ9(X/X)) mice causes a severe reduction in the CoQ7 protein and a widespread CoQ deficiency and accumulation of demethoxyubiquinone. The deficit in CoQ induces a brain-specific impairment of mitochondrial bioenergetics performance, a reduction in respiratory control ratio, ATP levels and ATP/ADP ratio and specific loss of respiratory complex I. These effects lead to neuronal death and demyelinization with severe vacuolization and astrogliosis in the brain of CoQ9 (X/X) mice that consequently die between 3 and 6 months of age[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 826.8±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 41-43ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C54H82O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 795.227 |
| Flash Point | 314.4±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 794.621338 |
| PSA | 52.60000 |
| LogP | 18.89 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.525 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S22 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | DK4786000 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |