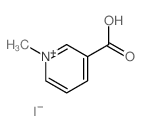
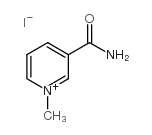
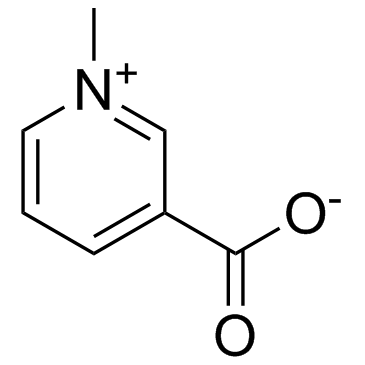
535-83-1
| Name | N-methylnicotinate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Betain nicotinate
Trigonelline N-methyl-3-carboxypyridinium Gynesis Coffearine Gynesine Pyridinium, 3-carboxy-1-methyl-, inner salt Trigenolline 1-methylpyridinium-3-carbonate Nicotinic acid N-methylbetaine 1-methyl-3-pyridinium carboxylate 1-Methylpyridinium-3-carboxylate Pyridinium, 3-carboxy-1-methyl-, hydroxide, inner salt Pyridinium, 3-carboxy-1-methyl-, hydroxide, inner salt (8CI) Caffearine 1-Methyl-3-pyridiniumcarboxylate Trigonellin Coffearin N-Methylnicotinate |
| Description | Trigonelline, an alkaloid with potential antidiabetic activity, is present in considerable amounts in coffee. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | It is found that Trigonelline (TG) significantly rescues the morphology of the H9c2 cells. Treatment of cells with Trigonelline attenuates H2O2 induced cell deaths and improves the antioxidant activity. In addition, Trigonelline regulates the apoptotic gene caspase-3, caspase-9 and anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2, Bcl-XL during H2O2 induced oxidative stress in H9c2 cells. For evident, flow cytometer results also confirms that Trigonelline significantly reduces the H2O2 induced necrosis and apoptosis in H9c2 cells. However, further increment of Trigonelline concentration against H2O2 can induce the necrosis and apoptosis along with H2O2[1]. |
| In Vivo | Trigonelline decreases bone mineralization and tends to worsen bone mechanical properties in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. In nicotinamide/streptozotocin-treated rats, Trigonelline significantly increases bone mineral density (BMD) and tends to improve cancellous bone strength. Trigonelline differentially affects the skeletal system of rats with streptozotocin-induced metabolic disorders, intensifying the osteoporotic changes in streptozotocin-treated rats and favorably affecting bones in the non-hyperglycemic (nicotinamide/streptozotocin-treated) rats[2]. |
| Cell Assay | The H9c2 cells are seeded in the 96 well at a density of 1×105 cells/well. The cells are treated with different concentrations of Trigonelline (TG) (25 to 150 μM) and hydrogen peroxide (25 to 125 μM). It is incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 incubator for 24 h and 6 h respectively and then the culture is treated with the water soluble tetrazolium (WST) reagent incubated for 2 h to 4 h. The living cells absorb the WST then it is converted into an orange colour product. Then, the intensity of colour is measured at 450 nm using spectra count ELISA reader. For cardio protective activity, the cells are seeded and separated into six groups control, H2O2 alone, the rest of groups’ initially exposed to different concentration (25 to 125 μM) of Trigonelline for 48 hours. Then, 100 μM of H2O2 is added and incubated for 4 hours, after, read the absorbance at 450 nm for cell viability assay[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Three-month-old female Wistar rats are used in this study. The animals are divided into five groups (n=10): Control rats, Streptozotocin-treated control rats, Streptozotocin-treated rats receiving Trigonelline (50 mg/kg p.o. daily), Nicotinamide/streptozotocin-treated control rats, and Nicotinamide/streptozotocin-treated rats receiving Trigonelline (50 mg/kg p.o. daily). Administration of Trigonelline starts two weeks after streptozotocin and lasts four weeks. Trigonelline is administered once daily by a stomach tube. All control rats receive tap water (the vehicle) at the same volume of 2 mL/kg p.o. The four-week period of Trigonelline administration is long enough to demonstrate skeletal effects of Trigonelline and other compounds of plant origin in rats. The rats are fasted overnight after the last Trigonelline or vehicle administration. The next day, the blood glucose level is measured and the rats are anesthetized with ketamine and xylazine, and then sacrificed by cardiac exsanguination[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2528 (rough estimate) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 251.96°C (rough estimate) |
| Melting Point | 260ºC (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H7NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 137.136 |
| Exact Mass | 137.047684 |
| PSA | 44.01000 |
| LogP | -3.91 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.554 |
| Storage condition | 2~8℃ |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
|
~% 
535-83-1
Detail
|
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 119, # 22 p. 5091 - 5094 |
|
~% 
535-83-1 |
| Literature: Monatshefte fuer Chemie, , vol. 22, p. 373 Monatshefte fuer Chemie, , vol. 21, p. 927 Anm. Monatshefte fuer Chemie, , vol. 24, p. 200 |
|
~% 
535-83-1 |
| Literature: Journal fuer Praktische Chemie (Leipzig), , vol. <2> 130, p. 11,18 |
|
~% 
535-83-1 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron, , vol. 36, p. 785 - 789 |
|
~% 
535-83-1 |
| Literature: Tetrahedron, , vol. 36, p. 785 - 789 |
|
~% 
535-83-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Molecular Structure, , vol. 614, # 1-3 p. 97 - 108 |
|
~% 
535-83-1 |
| Literature: Chemische Berichte, , vol. 77/79, p. 362,365 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |