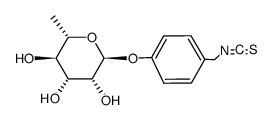
73255-40-0
| Name | glucomoringin isothiocyanate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
4-(α-L-rhamnopyranosyloxy)benzyl isothiocyanate
4-(α-L-Rhamnosyloxy)benzyl isothiocyanate 4(α-L-rhamnosyloxy)-benzyl isothiocyanate [4-(α-L-rhamnosyloxy)benzyl]isothiocyanate GMG-ITC (4-[(α-L-rhamnosyloxy)benzyl]isothiocyanate) |
| Description | Moringin is a potent and selective TRPA1 ion channel natural agonist with an EC50 of 3.14 μM. Moringin does not activate or activates very weakly the vanilloids somatosensory channels TRPV1, TRPV2, TRPV3 and TRPV4, and the melastatin cooling receptor TRPM8. Moringin has hypoglycemic, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anticancer and neuroprotection activities[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | 在 SH-SY5Y 人神经母细胞瘤细胞中,Moringin(16.4 µM;24-72 小时)以时间和浓度依赖性方式显着降低 SH-SY5Y 细胞生长[2]。 Moringin (1.64-8.2 μM; 24 h) 在 SH-SY5Y 细胞中增加 p53、p21 和 Bax 在蛋白质和转录水平的表达。 Moringin 显著增加 caspase 3/9 的基因表达并增强它们的切割,从而启动内在的细胞凋亡级联反应[2]。 Moringin 抑制 NF-κB 的核转位[2]。 |
| In Vivo | 在实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎 (EAE) 小鼠中,Moringin (10 mg/kg;腹腔注射;每天 1 次,共 5 周) 预处理可使异常的 Wnt-β-catenin 通路正常化,导致 GSK3β 抑制和 β-catenin 上调,从而调节 T 细胞活化 ( CD4 和 FoxP3),通过激活 PPARγ 抑制主要的炎症介质 (IL-1β、IL-6 和 COX2)。 辣木苷增加 EAE 小鼠体内抗氧化 Nrf2 的表达[3]。 |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C14H17NO5S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 311.35300 |
| Exact Mass | 311.08300 |
| PSA | 123.60000 |
| LogP | 0.49570 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |