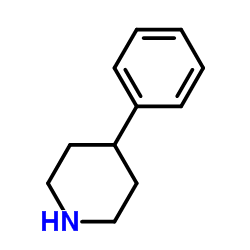
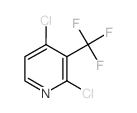
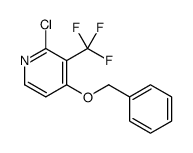
1254977-87-1
| Name | 3-(Cyclopropylmethyl)-7-(4-phenyl-1-piperidinyl)-8-(trifluorometh yl)[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyridine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
3-(cyclopropylmethyl)-7-(4-phenyl-1-piperidinyl)-8-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]pyridine
4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-2-(4-hydroxybutyn-1-yl)-1-(3-phenylpropyl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)imidazole 4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-2-(4-hydroxybutyn-1-yl)-1-(3-phenylpropyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)imidazole 3-(cyclopropylmethyl)-7-(4-phenylpiperidin-1-yl)-8-(trifluoromethyl)[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyridine 1-[(5-CHLORO-1H-INDOL-2-YL)CARBONYL]-4-METHYL-PIPERAZINE 4-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(3-phenylpropyl)-5-(4-pyridinyl)-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-3-butyn-1-ol (5-chloro-1H-indol-2-yl)-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-yl)methanone 4-(4-Fluorophenyl)-2-(4-hydroxy-1-butynyl)-1-(3-phenylpropyl)-5-(pyridin-4-yl)imidazole 4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(4-hydroxy-1-butynyl)-1-(3-phenylpropyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)imidazole JNJ-42153605 |
| Description | JNJ-42153605 is a positive allosteric modulator of the metabotropic glutamate 2 (mGlu2) receptor with an EC50 of 17 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
EC50: 17 nM (mGlu2 PAM)[1] |
| In Vitro | JNJ-42153605 is assessed for its selectivity for the mGlu2 receptor and is found to not have agonist or antagonist activity toward other mGlu receptor subtypes up to 30 μM. JNJ-42153605 shows high permeability with no indication for P-glycoprotein efflux[1]. |
| In Vivo | JNJ-42153605 shows a central in vivo efficacy by inhibition of REM sleep state at a dose of 3 mg/kg po in the rat sleep-wake EEG paradigm, a phenomenon shown to be mGlu2 mediated. In mice, JNJ-42153605 shows reversed PCP-induced hyperlocomotion with an ED50 of 5.4 mg/kg sc, indicative of antipsychotic activity. JNJ-42153605 shows a rapid rate of absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, reaching the maximal concentration after 0.5 h. Clearance in vivo is moderate to high in both rat and dog (35 and 29 mL/min/kg, respectively). Elimination halflives are on the shorter side across the species, being 2.7 h in rat and 0.8-1.1 h in dog[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: The effects of the tested molecule and vehicle on sleep−wake distribution during the lights-on period are investigated in 16 rats. Two EEG recording sessions are performed: the first recording session starts at 13:30 h and lasts 20 h following oral administration of saline. The second recording session is performed during the same consecutive circadian time and for the same duration following administration of either vehicle (20% CD+2H2T) or JNJ-42153605[1]. Mice: Male NMRI mice are treated with vehicle, or JNJ-42153605, and immediately challenged with either PCP (5.0 mg/kg, sc) or vehicle and individually placed into open-fields for a 30 min period. The distance traveled by animals is measured using video tracking and computerized analysis systems[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C22H23F3N4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 400.44000 |
| Exact Mass | 400.18700 |
| PSA | 33.43000 |
| LogP | 5.14960 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
|
~48% 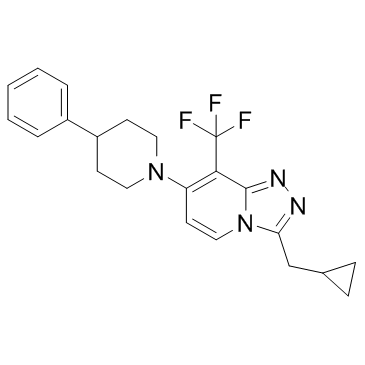
1254977-87-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 55, # 20 p. 8770 - 8789 |
|
~% 
1254977-87-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 55, # 20 p. 8770 - 8789 |
|
~% 
1254977-87-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 55, # 20 p. 8770 - 8789 |
|
~% 
1254977-87-1 |
| Literature: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, , vol. 55, # 20 p. 8770 - 8789 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |