912545-86-9
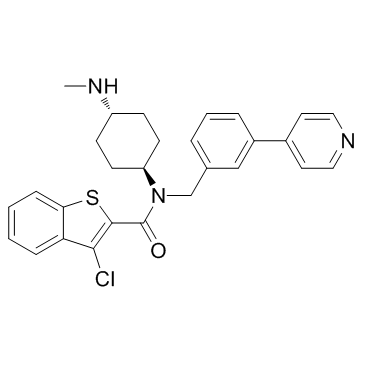
| Name | 3-chloro-N-[4-(methylamino)cyclohexyl]-N-[(3-pyridin-4-ylphenyl)methyl]-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
[3H]SAG-1.3
Benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxamide, 3-chloro-N-[trans-4-(methylamino)cyclohexyl]-N-[[3-(4-pyridinyl)phenyl]methyl]- Smoothened agonist 3-Chloro-N-[trans-4-(methylamino)cyclohexyl]-N-[[3-(4-pyridinyl)phenyl]methyl]-benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxamide 3-Chloro-N-[trans-4-(methylamino)cyclohexyl]-N-[3-(4-pyridinyl)benzyl]-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxamide SAG.HCI SAG |
| Description | SAG is a potent Smo receptor agonist which activates the Hedgehog signaling pathway with a Kd of 59 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Kd: 59 nM (Smo)[1] |
| In Vitro | SAG acts downstream of Ptch1 in the Hh pathway and counteracts cyclopamine inhibition of Smo. SAG induces firefly luciferase expression in Shh-LIGHT2 cells with an EC50 of 3 nM and then inhibits expression at higher concentrations. In Smo-expressing Cos-1 cells, SAG yields an apparent dissociation constant (KD) of 59 nM for the SAG/Smo complex[1]. SAG and purmorphamine verride the inhibitory effect of robotnikinin since Smo functions downstream of Shh/Ptc1[2]. |
| In Vivo | In CD-1 mice, SAG (1.0 mM) or NELL-1 (600 μg/ml) alone results in increased bone formation at 4 and 8 weeks, but significantly greater bone formation with both components combined (SAG + NELL-1). The combination of the two compounds exhibits a significant increase in new bone formation, accompanied by increased defect vascularization[3]. SAG (15, 17, or 20 mg/kg, i.p.) induces pre-axial polydactyly prevalently. The highest SAG dose is effective in ca. 80% of the embryos and increased Gli1 and Gli2 mRNA expression in the limb bud, with Gli1 mRNA being the most upregulated[4]. |
| Animal Admin | GD 9:6 hr females are weighed, given a single intraperitoneal SAG injection (6, 6, and 7 for the 15, 17, and 20 mg/kg doses, respectively) or vehicle (lactated Ringer's solution; 9 litters), and returned to their home cage. GD 9:6 is a sensitive period for inducing forelimb malformations by retinoic acid and ethanol administration. For SAG dose-response studies, GD 15 embryos are collected, examined for the number and appearance of the digits on each limb. For whole-mount in situ hybridization studies, embryos are collected at GD 9:10 hr in ice-cold RNase-free phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, rinsed with PBS, dehydrated in methanol and stored at -20°C. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 688.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C28H28ClN3OS |
| Molecular Weight | 490.059 |
| Flash Point | 370.3±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 489.164154 |
| PSA | 73.47000 |
| LogP | 6.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.678 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
|
~% 
912545-86-9 |
| Literature: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters, , vol. 19, # 15 p. 4308 - 4311 |
