7659-95-2
| Name | betanin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(s-(r*,r*))--dihydro-6-hydroxy-1h-indol-1-yl)ethenyl)-3-dihydro
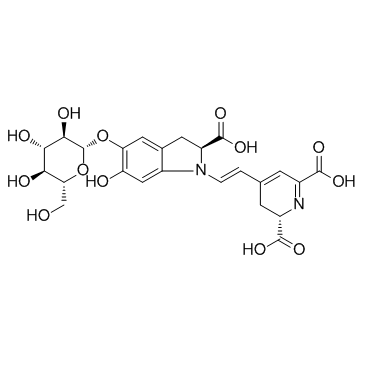
(Red Beet extract diluted with Dextrin) Phytolaccanin (2S)-4-{2-[(2S)-2-Carboxy-5-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-6-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-1-yl]vinyl}-2,3-dihydro-2,6-pyridinedicarboxylic acid Beetroot Red EINECS 231-628-5 2,6-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 4-[2-[(2S)-2-carboxy-5-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-2,3-dihydro-6-hydroxy-1H-indol-1-yl]ethenyl]-2,3-dihydro-, (2S)- Betanin (Red Beet extract diluted with Dextrin) |
| Description | Betanin has potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect, that could inhibit peroxynitrite (ONOO-), with an IC50 of 19.2 μM. Betanin is a red glycoside obtained from beets that can be used as colorant. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 19.2 μM (ONOO-)[1]. |
| In Vitro | Betanin is a representative constituent of red beetroot betacyanins, could inhibit peroxynitrite (ONOO-), with an IC50 of 19.2 μM[1]. Betanin also has anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative effects, nephroprotective activity, cardioprotective activity, strong, antioxidant and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity[2]. Another study is also indicated the protective effect of Betanin against high glucose induced rat renal epithelial cell fibrosis and matrix accumulation, major features of diabetic nephropathy (DN)[2]. |
| In Vivo | Betanin can inhibit the fructose-induced diabetic cardiac fibrosis and paraquat induced acute kidney toxicity[2]. The co-administration of Betanin (20 mg/kg b.w.) to diabetic rats prevent significantly the raise of glucose level and also reverse the levels of insulin compared with untreated diabetic rats. Interestingly diabetic rats treated with Betanin (20 mg/kg b.w.) and glibenclamide portray the significant changes in the body weight compared to diabetic control. HbA1c levels significantly increases in diabetic rats and when treated with Betanin as well as glibenclamide. Treatment with Betanin as well as glibenlamide to STZ-NA induces diabetic rat’s elicit significant decreases in those levels when compared with diabetic control rats[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[3] Healthy adult Male albino Wistar strain (Rattus norvegicus, 90-120 days of age) are used in the current study. After the successful induction of experimental diabetes, the rats are divided into four groups each comprising a minimum of six rats a total of 30 rats (18 diabetic surviving rats, 12 normal rats). Betanin is administered via oral intubation to the experimental rats using a gavage needle daily for a period of 30 days. Group 1: Normal Control rats. Group 2: Rats treated with Betanin (20 mg/kg b.w.) alone. Group 3: Diabetic Control rats. Group 4: Rats treated with STZ-NA by i.p. and Betanin (20 mg/kg b.w.). Group 5: Rats treated with STZ-NA by i.p. and glibenclamide (600 μg/kg b.w.)[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 983.5±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C24H26N2O13 |
| Molecular Weight | 550.469 |
| Flash Point | 548.6±37.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 550.143494 |
| PSA | 249.38000 |
| LogP | -4.49 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.740 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | 2261.0 |
| RTECS | US7968100 |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 3203001990 |
| HS Code | 3203001990 |
|---|