15690-57-0
| Name | trans-clomiphene |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
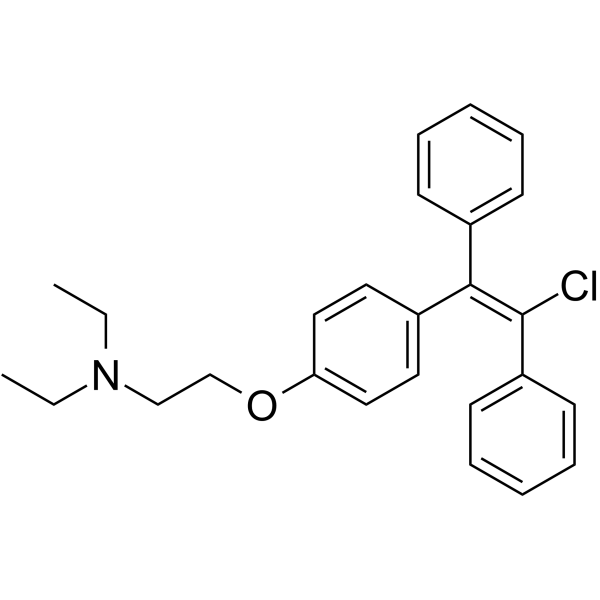
2-(4-(2-Chloro-1,2-diphenylvinyl)phenoxy)-N,N-diethylethanamine
Clomiphene Zuclomiphene Isomer A Transclomifenum 2-(4-(2-chloro-1,2-diphenylethenyl)phenoxy)-N,N-diethylethanamine zuclomifene Ethanamine, 2-(4-(2-chloro-1,2-diphenylethenyl)phenoxy)-N,N-diethyl- cis-clomifene 2-[4-(2-chloro-1,2-diphenylethenyl)phenoxy]-N,N-diethylethanamine cis-clomiphene enclomiphene Ethanamine, 2-[4-[(E)-2-chloro-1,2-diphenylethenyl]phenoxy]-N,N-diethyl- Transclomiphene 1-[p-(b-Diethylaminoethoxy)phenyl]-1,2-diphenylchloroethylene Clomiphene B trans-Clomiphene (E)-Clomiphene 2-[p-(2-Chloro-1,2-diphenylvinyl)phenoxy]triethylamine (E)-2-(4-(2-Chloro-1,2-diphenylethenyl)phenoxy)-N,N-diethylethanamine trans-Clomifene 2-[p-(b-Chloro-a-phenylstyryl)phenoxy]triethylamine Z-CloMiphene-d4 2-{4-[(E)-2-Chloro-1,2-diphenylvinyl]phenoxy}-N,N-diethylethanamine 2-{4-[(E)-2-chloro-1,2-diphenylethenyl]phenoxy}-N,N-diethylethanamine |
| Description | Enclomiphene ((E)-Clomiphene) is a potent and orally active non-steroidal estrogen receptor antagonist, with antioestrogenic property. Enclomiphene can be used for the research of ovarian dysfunction, testosterone deficiency, male hypogonadism and type 2 diabetes[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Enclomiphene (0-100 μM, 6 h) dose-dependently inhibits basal and gonadotrophin-stimulated small and large ovine luteal cell progesterone secretion[2]. Enclomiphene (0-100 μg/mL, 24 h) dose-dependently inhibits fertilization rates, blastocyst formation rates, and degeneration rates in mouse oocytes[3]. Enclomiphene (1 nM-10 μM, 6 h) dose-dependently decreases E2-induced inhibition of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) secretion in primary sheep pituitary cells[4]. |
| In Vivo | Enclomiphene (subcutaneous injection, 0.25 and 0.5 mg/animal, daily) inhibits spermatogenesis and decreases serum luteinizing hormone (LH) and testosterone levels in intact or castrated rats[5]. Enclomiphene (oral adminstration, 0.03-3 mg/kg, daily for 90 days) reductes body weight to sham levels, and reduced serum cholesterol[6]. Animal Model: 21 days-old Charles River male rats[5] Dosage: 0.25 and 0.5 mg/animal, daily for 24 days. Administration: Subcutaneous injection Result: Decreased LH and testosterone levels in the serum. Animal Model: OVX (ovariectomy) rat model[6] Dosage: 0.03, 1, and 3 mg/kg, daily for 90 days. Administration: Oral adminstration Result: Reducted body weight to sham levels, and reduced serum cholesterol. Showed dose-dependent effects on the proximal tibia with BMD and BMC approaching posttreatment Sham levels. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 509.0±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C26H28ClNO |
| Molecular Weight | 405.960 |
| Flash Point | 261.6±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 405.185944 |
| PSA | 12.47000 |
| LogP | 8.01 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.588 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|