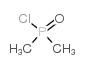
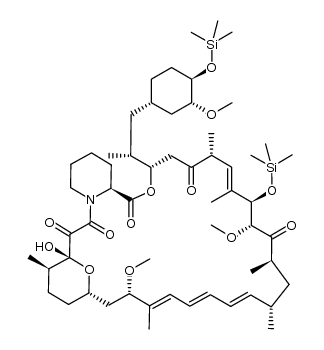
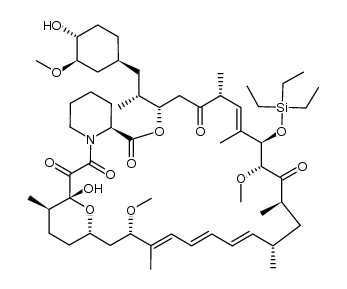
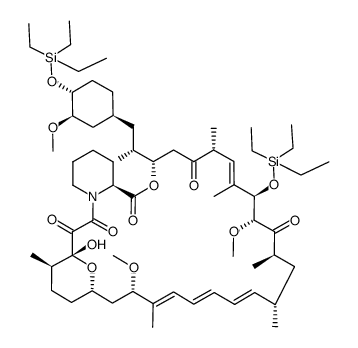
572924-54-0
| Name | ridaforolimus |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
(1R,2R,4S)-4-{(2R)-2-[(1R,9S,12S,15R,16E,18R,19R,21R,23S,24E,26E,28E,30S,35R)-1,18-Dihydroxy-19,30-dimethoxy-15,17,21,23,29,35-hexamethyl-2,3,10,14,20-pentaoxo-11,36-dioxa-4-azatricyclo[30.3.1.0] hexatriaconta-16,24,26,28-tetraen-12-yl]propyl}-2-methoxycyclohexyl dimethylphosphinate
Phosphinic acid, P,P-dimethyl-, (1R,2R,4S)-2-methoxy-4-[(2R)-2-[(3S,6R,7E,9R,10R,12R,14S,15E,17E,19E,21S,26R,27R,34aS)-1,4,5,6,9,10,11,12,13,14,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,31,32,33,34,34a-tetracosahydro-9,27-dihydroxy-10,21-dimethoxy-6,8,12,14,20,26-hexamethyl-1,5,11,28,29-pentaoxo-23,27-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclohentriacontin-3-yl]propyl]cyclohexyl ester Deforolimus Ridaforolimus |
| Description | Deforolimus (AP23573; MK-8669) is a potent and selective mTOR inhibitor; inhibits ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation with an IC50 of 0.2 nM in HT-1080 cells. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
mTOR |
| In Vitro | Treatment of HT-1080 fibrosarcoma cells with deforolimus results in a dose-dependent inhibition of phosphorylation of both S6 and 4E-BP1, with IC50s of 0.2 and 5.6 nM, respectively, and EC50s of 0.2 and 1.0 nM, respectively. In HT-1080 cells, the EC50 for inhibition of cell proliferation (0.5 nM) is similar to the EC50s for inhibition of S6 and 4E-BP1 phosphorylation. Exposure to deforolimus reduces the proliferation of cell lines representing a variety of tumor types. Administration of deforolimus to tumor cells in vitro elicit dose-dependent inhibition of mTOR activity with concomitant effects on cell growth and division. Deforolimus exhibits a predominantly cytostatic mode of action, consistent with the findings for other mTOR inhibitors. Potent inhibitory effects on vascular endothelial growth factor secretion, endothelial cell growth, and glucose metabolism[1]. |
| In Vivo | Deforolimus inhibits tumor growth in mice bearing PC-3 (prostate), HCT-116 (colon), MCF7 (breast), PANC-1 (pancreas), or A549 (lung) xenografts. Deforolimus inhibits tumor growth in a dose-dependent manner, with 0.3 mg/kg being the lowest dose that inhibits tumor growth significantly and 3 and 10 mg/kg doses achieving maximum inhibition[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Cells are treated with 10-fold serial dilutions of deforolimus (1,000 to 0.0001 nM) or vehicle (ethanol). Following 72 hours culture at 37°C, the plates are aspirated and stored at −80°C for proliferation analysis[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: Animals selected with tumors in the proper size range are assigned to various treatment groups. Deforolimus, at dosages of 3 and 10 mg/kg, is administered i.p. on 2 different treatment schedules: (a) daily, 5 continuous days every other week and (b) once weekly. The control group is untreated[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 996.2±75.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 95-98ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C53H84NO14P |
| Molecular Weight | 990.206 |
| Flash Point | 556.3±37.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 989.562927 |
| PSA | 211.31000 |
| LogP | 3.12 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.539 |
| Storage condition | Hygroscopic, -20?C Freezer, Under Inert Atmosphere |
|
~% 
572924-54-0 |
| Literature: US2004/73024 A1, ; Page 38 ; |
|
~83% 
572924-54-0 |
| Literature: US2014/58081 A1, ; Paragraph 0047 ; |
|
~% 
572924-54-0 |
| Literature: US2014/58081 A1, ; |
|
~% 
572924-54-0 |
| Literature: US2014/58081 A1, ; |
|
~% 
572924-54-0 |
| Literature: US2014/58081 A1, ; |
|
~% 
572924-54-0 |
| Literature: US2014/58081 A1, ; |
|
~% 
572924-54-0 |
| Literature: US2014/58081 A1, ; |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |