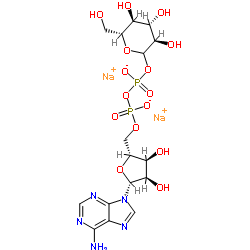
102129-65-7
| Name | adenosine-5'-diphosphoglucose |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
MFCD00056005
ADP-glc,ADP-Glucose,ADPG ADENOSINE 5'-DIPHOSPHOGLUCOSE DISODIUM ADP-Glucose/ADP-glc/ADPG adp-glc |
| Description | ADP-Glucose disodium is an immediate precursor used for the biosynthesis of storage polysaccharides in plants, green algae, and cyanobacteria, and structural polysaccharides in some bacteria, by the addition of glucose. [1], [2] It is used to produce amylose, amylopectin, starch and other polysaccharides by amylose synthase or starch synthase in plastids. ADPG is usually produced in plastids, although it can be biosynthesized in the cytoplasm of some grasses and imported into plastids by membrane-bound transporters. [3] References: [1]. Ball, SG and Morell, MK From bacterial glycogen to starch: understanding the biogenesis of plant starch granules. Annu. Rev. Plant Biology. 54, 207-233 (2003). [2]. Sambou, T., Dinadayala, P., Stadthagen, G. et al. Capsular glucan and intracellular glycogen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: biosynthesis and implications for mouse survival. Molecular Microbiology 70(3), 762-774 (2008).[3]. Comparot-Moss, S. and Denyer, K. Evolution of the starch biosynthetic pathway in cereals and other grasses. Journal of Experimental Botany 60(9), 2481-2492 (2009). |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Molecular Formula | C16H23N5Na2O15P2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 633.305 |
| Exact Mass | 633.046143 |
| PSA | 344.87000 |
| Storage condition | -20C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |