Azobenzene
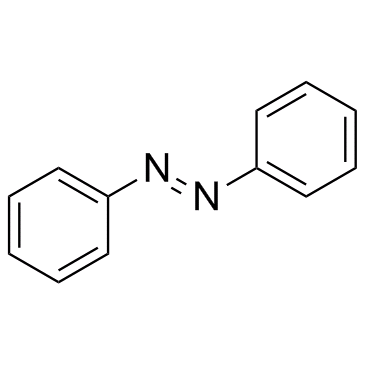
Azobenzene structure
|
Common Name | Azobenzene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 103-33-3 | Molecular Weight | 182.221 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 293.0±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H10N2 | Melting Point | 66 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 122.9±19.6 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of AzobenzeneAzobenzene can be used as an optical trigger for the design and synthesis of a large variety of photoresponsive systems. |
| Name | azobenzene |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Azobenzene can be used as an optical trigger for the design and synthesis of a large variety of photoresponsive systems. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Photochromic compounds that undergo large conformational changes when exposed to light of appropriate wavelength are particularly attractive as molecular switch elements. Azobenzene is a popular choice among the chromophores. The thermodynamically favored trans isomer is rapidly converted to the cis isomer by irradiation at the wavelength of the π-π* transition, whereas the reverse process is achieved either (slowly) by thermal relaxation in the dark or (quickly) by irradiation at the wavelength of the n-π* transition. The azobenzene amino acid (aa) can be used as a photo-inducible conformational switch in polypeptides. A reversible conformational change of the peptide backbone is induced by switching between the cis and trans configurations of the azobenzene moiety by irradiation with light of suitable wavelength[1]. Azobenzene has been the most widely used optical trigger for the synthesis of photoresponsive systems ranging from poly-a-amino acids to innovative materials with light-controlled mechanical and optical properties. Its use in form of appropriate derivatives allow to generate cyclic peptide structures of constraint conformational space and thus to exploit its reversible photoisomerization to induce well defined transitions between different conformational states[2]. Azobenzene photoswitches can be used to drive functional changes in peptides, proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates[3]. |
| References |
[3]. Beharry AA, et al. Azobenzene photoswitches for biomolecules. Chem Soc Rev. 2011 Aug;40(8):4422-37. |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 293.0±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 66 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C12H10N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 182.221 |
| Flash Point | 122.9±19.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 182.084396 |
| PSA | 24.72000 |
| LogP | 3.82 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.575 |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Air and light sensitive. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H332-H341-H350-H373-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P273-P281-P308 + P313-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T,N,Xn,F |
| Risk Phrases | R45 |
| Safety Phrases | S53-S45-S60-S61-S62-S36/37-S33-S29-S16-S9-S7 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CN1400000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| HS Code | 2927000090 |
|
~% 
Azobenzene CAS#:103-33-3 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 103, # 22 p. 6599 - 6603 |
| HS Code | 2927000090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2927000090 other diazo-, azo- or azoxy-compounds。Supervision conditions:None。VAT:17.0%。Tax rebate rate:9.0%。MFN tariff:6.5%。General tariff:30.0% |
|
Photoswitching a molecular catalyst to regulate CO2 hydrogenation.
Dalton Trans. 44 , 14854-64, (2015) Inspired by nature's ability to regulate catalysis using physiological stimuli, azobenzene was incorporated into Rh(bis)diphosphine CO2 hydrogenation catalysts to photoinitiate structural changes to m... |
|
|
A charged aerosol detector/chemiluminescent nitrogen detector/liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry system for regular and fragment compound analysis in drug discovery.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1411 , 63-8, (2015) In this paper, we introduce a high throughput LCMS/UV/CAD/CLND system that improves upon previously reported systems by increasing both the quantitation accuracy and the range of compounds amenable to... |
|
|
Rheological profiling of organogels prepared at critical gelling concentrations of natural waxes in a triacylglycerol solvent.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 4862-9, (2015) The aim of this study was to use a detailed rheological characterization to gain new insights into the gelation behavior of natural waxes. To make a comprehensive case, six natural waxes (differing in... |
| Azobenzeen |
| Benzofume |
| 1,2-Diphenyldiazene |
| Azobenzene, (E)- |
| AZOBENZOL |
| Diazene, 1,2-diphenyl-, (E)- |
| Azofume |
| Diphenyldiazene |
| Azobenzen |
| (E)-Diphenyldiazene |
| EINECS 203-102-5 |
| MFCD00003022 |
| DIAZENE, DIPHENYL-, (E)- |
| (E)-1,2-diphenyldiazene |
| ENT 14,611 |
| Azobenzene |