Daptomycin
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 08:16:08
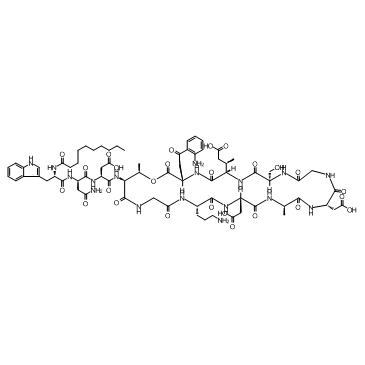
Daptomycin structure
|
Common Name | Daptomycin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 103060-53-3 | Molecular Weight | 1620.671 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 2078.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C72H101N17O26 | Melting Point | 202-204?C | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 1210.7±34.3 °C | |
Use of DaptomycinDaptomycin is a lipopeptide antibiotic with rapid in vitro bactericidal activity against gram-positive organisms. |
| Name | daptomycin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Daptomycin is a lipopeptide antibiotic with rapid in vitro bactericidal activity against gram-positive organisms. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Daptomycin has excellent in-vitro inhibitory and bactericidal activity against nafcillin-susceptible and resistant staphylococci (MIC90 less than or equal to 0.5 mg/L) and against enterococci (MIC90 less than or equal to 2.0 mg/L). Daptomycin is more active than vancomycin against the majority of isolated tested. With the exception of trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole, daptomycin is the most active agent in vitro against enterococci, and is the most active against nafcillin-resistant staphylococci. Daptomycin and vancomycin show a marked increase in MIC when the inoculum is increased from 105 to 107 cfu/mL[1]. Daptomycin is effective within a very narrow range of drug concentrations (from 0.125 to 2.0 tLg/mL) and is more active than other agents tested against S. faecalis[2]. Daptomycin inhibits the formation of these nucleotide-linked intermediates[3]. |
| In Vivo | At a dose of 10 mg/kg given twice daily, daptomycin reduces the number of organisms per kidney significantly compared with that in infected untreated controls within 48 h after the initiation of therapy. At 20 mg/kg given once a day, daptomycin is less effective but reduces colony counts significantly after 4 days of therapy, and its activity is comparable to that of vancomycin or vancomycin-gentamicin given twice daily[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Inocula containing 109 CFU/mL are prepared from an 18-h brain heart infusion broth culture. The exact number in each inoculum is subsequently determined by the standard serial 10-fold dilution agar pour plate technique. Animals are challenged intravenously with a 1.0-mL inoculum. This inoculum is known to infect the renal medulla of normal rats. Twenty-four hours later the animals are divided into eight groups and are given either saline only (controls) or antibiotic therapy initiated with Daptomycin at 10 mg/kg (Daptomycin10), Daptomycin at 20 mg/kg (Daptomycin20), Daptomycin10 plus gentamicin at 1.5 mg/kg, vancomycin at 20 mg/kg, vancomycin at 20 mg/kg plus gentamicin at 1.5 mg/kg, ampicillin at 30 mg per rat per injection, and ampicillin at 30 mg per rat plus gentamicin at 1.5 mg/kg. Animals receive Daptomycin20 once daily; all other drugs are administered twice daily. Vancomycin and Daptomycin are given subcutaneously; ampicillin and gentamicin are given intramuscularly. Drugs are administered for up to 13 days. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 2078.2±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 202-204?C |
| Molecular Formula | C72H101N17O26 |
| Molecular Weight | 1620.671 |
| Flash Point | 1210.7±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 1619.710327 |
| PSA | 702.02000 |
| LogP | -4.07 |
| Appearance of Characters | colorless to faint yellow |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.638 |
| Storage condition | Store at -20°C |
| Water Solubility | methanol: soluble5mg/mL |
| RTECS | HB5626000 |
|---|
| N-decanoyl-L-tryptophyl-L-asparaginyl-N-[(3S,6S,9R,15S,18R,21S,24S,30S,31R)-3-[2-(2-aminophenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-24-(3-aminopropyl)-15,21-bis(carboxymethyl)-6-[(1R)-2-carboxy-1-methylethyl]-9-(hydroxymethyl)-18,31-dimethyl-2,5,8,11,14,17,20,23,26,29-decaoxo-1-oxa-4,7,10,13,16,19,22,25,28-nonaazacyclohentriacontan-30-yl]-L-α-asparagine |
| N-Decanoyl-L-tryptophyl-L-asparaginyl-N-[(3S,6S,9R,15S,18R,21S,24S,30S,31R)-3-[2-(2-aminophenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-24-(3-aminopropyl)-15,21-bis(carboxymethyl)-6-[(2R)-1-carboxypropan-2-yl]-9-(hydroxymethyl)-18,31-dimethyl-2,5,8,11,14,17,20,23,26,29-decaoxo-1-oxa-4,7,10,13,16,19,22,25,28-nonaazacyclohentriacontan-30-yl]-L-α-asparagine |
| N-Decanoyl-L-tryptophyl-L-asparaginyl-N-[(3S,6S,9R,15S,18R,21S,24S,30S,31R)-3-[2-(2-aminophenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-24-(3-aminopropyl)-15,21-bis(carboxymethyl)-6-[(2R)-1-carboxy-2-propanyl]-9-(hydroxymethyl) ;-18,31-dimethyl-2,5,8,11,14,17,20,23,26,29-decaoxo-1-oxa-4,7,10,13,16,19,22,25,28-nonaazacyclohentriacontan-30-yl]-L-α-asparagine |
| Daptomycin |
| L-α-Asparagine, N-(1-oxodecyl)-L-tryptophyl-L-asparaginyl-N-[(3S,6S,9R,15S,18R,21S,24S,30S,31R)-3-[2-(2-aminophenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-24-(3-aminopropyl)-15,21-bis(carboxymethyl)-6-[(1R)-2-carboxy-1-met hylethyl]-9-(hydroxymethyl)-18,31-dimethyl-2,5,8,11,14,17,20,23,26,29-decaoxo-1-oxa-4,7,10,13,16,19,22,25,28-nonaazacyclohentriacont-30-yl]- |
| Deptomycin |
| L-α-asparagine, N-(1-oxodecyl)-L-tryptophyl-L-asparaginyl-N-[(3S,6S,9R,15S,18R,21S,24S,30S,31R)-3-[2-(2-aminophenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-24-(3-aminopropyl)-15,21-bis(carboxymethyl)-6-[(1R)-2-carboxy-1-methylethyl]-9-(hydroxymethyl)-18,31-dimethyl-2,5,8,11,14,17,20,23,26,29-decaoxo-1-oxa-4,7,10,13,16,19,22,25,28-nonaazacyclohentriacont-30-yl]- |
| Cubicin |
| (3S)-3-{[(2S)-4-amino-2-{[(2S)-2-(decanoylamino)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoyl]amino}-4-oxobutanoyl]amino}-4-{[(3S,6S,9R,15S,18R,21S,24S,30S,31R)-3-[2-(2-aminophenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-24-(3-aminopropyl)-15,21-bis(carboxymethyl)-6-[(1R)-2-carboxy-1-methylethyl]-9-(hydroxymethyl)-18,31-dimethyl-2,5,8,11,14,17,20,23,26,29-decaoxo-1-oxa-4,7,10,13,16,19,22,25,28-nonaazacyclohentriacontan-30-yl]amino}-4-oxobutanoic acid |
| Daptomycin,N-(1-Oxodecyl)-L-tryptophyl-D-asparaginyl-L-α-aspartyl-L-threonylglycyl-L-ornithinyl-L-α-aspartyl-D-alanyl-L-α-aspartylglycyl-D-seryl-(3R)-3-methyl-L-α-glutamyl-α,2-diamino-γ-oxo-benzenebutanoicacid(13-4)lactone |
| LY146032 |
| CUBICIN DAPTOMYCIN |
| Cidecin |

