Mizolastine (dihydrochloride)
Modify Date: 2024-01-05 20:30:48
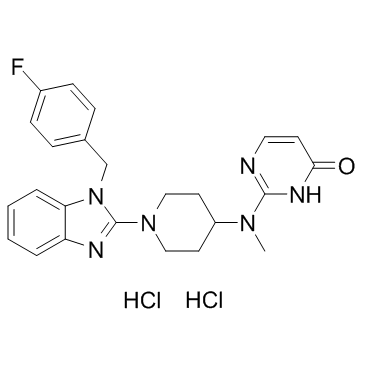
Mizolastine (dihydrochloride) structure
|
Common Name | Mizolastine (dihydrochloride) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1056596-82-7 | Molecular Weight | 505.415 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C24H27Cl2FN6O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Mizolastine (dihydrochloride)Mizolastine dihydrochloride is a histamine H1-receptor antagonist with IC50 of 47 nM used in the treatment of hay fever (seasonal allergic rhinitis), hives and other allergic reactions. Target: Histamine H1-receptorMizolastine is a histamine H1-receptor antagonist with IC50 of 47 nM used in the treatment of hay fever (seasonal allergic rhinitis), hives and other allergic reactions. It does not prevent the actual release of histamine from mast cells, just prevents it binding to receptors. Side effects can include dry mouth and throat.Mizolastine has demonstrated antiallergic effects in animals and healthy volunteers and anti-inflammatory activity in animal models. Double-blind trials have shown mizolastine to be significantly more effective than placebo and as effective as other second generation antihistamine agents, such as loratadine or cetirizine, in the management of patients with perennial or seasonal allergic rhinitis and in patients with chronic idiopathic urticaria. Available data also suggest that prophylactic administration of mizolastine is significantly more effective than placebo and as effective as prophylactic terfenadine in delaying the onset of symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis. |
| Name | Mizolastine dihydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Mizolastine dihydrochloride is a histamine H1-receptor antagonist with IC50 of 47 nM used in the treatment of hay fever (seasonal allergic rhinitis), hives and other allergic reactions. Target: Histamine H1-receptorMizolastine is a histamine H1-receptor antagonist with IC50 of 47 nM used in the treatment of hay fever (seasonal allergic rhinitis), hives and other allergic reactions. It does not prevent the actual release of histamine from mast cells, just prevents it binding to receptors. Side effects can include dry mouth and throat.Mizolastine has demonstrated antiallergic effects in animals and healthy volunteers and anti-inflammatory activity in animal models. Double-blind trials have shown mizolastine to be significantly more effective than placebo and as effective as other second generation antihistamine agents, such as loratadine or cetirizine, in the management of patients with perennial or seasonal allergic rhinitis and in patients with chronic idiopathic urticaria. Available data also suggest that prophylactic administration of mizolastine is significantly more effective than placebo and as effective as prophylactic terfenadine in delaying the onset of symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C24H27Cl2FN6O |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 505.415 |
| Exact Mass | 504.160736 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| 4(3H)-Pyrimidinone, 2-[[1-[1-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]-4-piperidinyl]methylamino]-, hydrochloride (1:2) |
| 2-[{1-[1-(4-Fluorobenzyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]-4-piperidinyl}(methyl)amino]-4(3H)-pyrimidinone dihydrochloride |
| Mizolastine (dihydrochloride) |